You cannot select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
|
|
7 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| resources | 7 years ago | |
| README.md | 7 years ago | |
| linked-list-1-introduction.go | 7 years ago | |
README.md
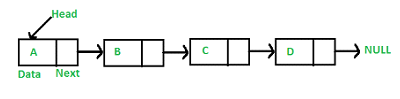
LinkedList | SET 1 (INTRODUCTION) Source
What It Is
Like arrays, LinkedList is a linear dat structure. Unlike arrays, LinkedList elements are not stored at contigous location; the elements are linked using pointers.
Why Linked List ?
Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have following limitations ;
-
- The size of the arrays is fixed. So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to upper limit irrespective of the usage.
-
- Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive, because room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to shifted.
Example
- ID[] = [1000, 1010, 1050, 2000, 2040]
And if we want to insert a new ID 10005, the to maintain the sorted order, we have to move all the elements after 1000 (excluding 1000).
Deletion is also expensive with arrays until unless some special techniques are used. For example, to delete 1010 in ID[], everythink after 1010 has to moved.
Advantages Over Arrays
-
- Dynamic size
-
- Ease of insertion/deletion
Drawbacks
-
- Random access is not allowed. We have to access elements sequientally starting from the first node. So we cannot do binary search with LinkedLists.
-
- Extra memory space for a pointer is required with each element of the list.