|
|
3 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| bip39 | 4 years ago | |
| btc | 4 years ago | |
| cmd/chantools | 3 years ago | |
| dataformat | 4 years ago | |
| doc | 4 years ago | |
| dump | 4 years ago | |
| lnd | 3 years ago | |
| .gitignore | 4 years ago | |
| .golangci.yml | 4 years ago | |
| LICENSE | 4 years ago | |
| Makefile | 4 years ago | |
| README.md | 3 years ago | |
| go.mod | 3 years ago | |
| go.sum | 3 years ago | |
| release.sh | 4 years ago | |
README.md
Channel tools
Index
This tool provides helper functions that can be used to rescue funds locked in
lnd channels in case lnd itself cannot run properly anymore.
WARNING: This tool was specifically built for a certain rescue operation and might not be well-suited for your use case. Or not all edge cases for your needs are coded properly. Please look at the code to understand what it does before you use it for anything serious.
WARNING 2: This tool will query public block explorer APIs for some
commands, your privacy might not be preserved. Use at your own risk or supply
a private API URL with --apiurl.
Installation
To install this tool, make sure you have go 1.13.x (or later) and make
installed and run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/guggero/chantools.git
cd chantools
make install
Channel recovery scenario
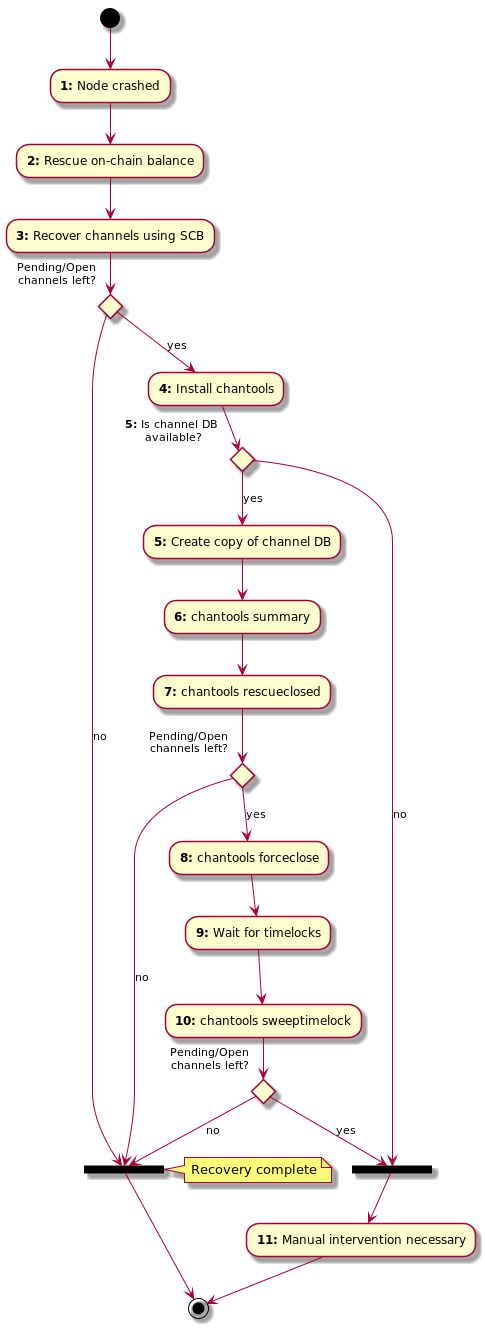
The following flow chart shows the main recovery scenario this tool was built
for. This scenario assumes that you do have access to the crashed node's seed,
channel.backup file and some state of a channel.db file (perhaps from a
file based backup or the recovered file from the crashed node).
Explanation:
-
Node crashed: For some reason your
lndnode crashed and isn't starting anymore. If you get errors similar to this, this or this, it is possible that a simple compaction (a full copy in safe mode) can solve your problem. Seechantools compactdb.
If that doesn't work and you need to continue the recovery, make sure you can at least extract thechannel.backupfile and if somehow possible any version of thechannel.dbfrom the node.
Whatever you do, do never, ever replace yourchannel.dbfile with an old version (from a file based backup) and start your node that way. Read this explanation why that can lead to loss of funds. -
Rescue on-chain balance: To start the recovery process, we are going to re-create the node from scratch. To make sure we don't overwrite any old data in the process, make sure the old data directory of your node (usually
.lndin the user's home directory) is safely moved away (or the whole folder renamed) before continuing.
To start the on-chain recovery, follow the sub step "Starting On-Chain Recovery" of this guide. Don't follow the whole guide, only this single chapter!
This step is completed once thelncli getinfocommand shows both"synced_to_chain": trueand"synced_to_graph": truewhich can take several hours depending on the speed of your hardware. Do not be alarmed that thelncli getinfocommand shows 0 channels. This is normal as we haven't started the off-chain recovery yet. -
Recover channels using SCB: Now that the node is fully synced, we can try to recover the channels using the Static Channel Backups (SCB). For this, you need a file called
channel.backup. Simply run the commandlncli restorechanbackup --multi_file <path-to-your-channel.backup>. This will take a while!. The command itself can take several minutes to complete, depending on the number of channels. The recovery can easily take a day or two as a lot of chain rescanning needs to happen. It is recommended to wait at least one full day. You can watch the progress with thelncli pendingchannelscommand. If the list is empty, congratulations, you've recovered all channels! If the list stays un-changed for several hours, it means not all channels could be restored using this method. One explanation can be found here. -
Install chantools: To try to recover the remaining channels, we are going to use
chantools. Simply follow the installation instructions. The recovery can only be continued if you have access to some version of the crashed node'schannel.db. This could be the latest state as recovered from the crashed file system, or a version from a regular file based backup. If you do not have any version of a channel DB,chantoolswon't be able to help with the recovery. See step 11 for some possible manual steps. -
Create copy of channel DB: To make sure we can read the channel DB, we are going to create a copy in safe mode (called compaction). Simply run
chantools compactdb --sourcedb <recovered-channel.db> --destdb ./results/compacted.db
We are going to assume that the compacted copy of the channel DB is located in./results/compacted.dbin the following commands. -
chantools summary: First,
chantoolsneeds to find out the state of each channel on chain. For this, a blockchain API (by default blockstream.info) is queried. The result will be written to a file called./results/summary-yyyy-mm-dd.json. This result file will be needed for the next command.
chantools --fromchanneldb ./results/compacted.db summary -
chantools rescueclosed: It is possible that by now the remote peers have force-closed some of the remaining channels. What we now do is try to find the private keys to sweep our balance of those channels. For this we need a shared secret which is called the
commit_pointand is changed whenever a channel is updated. We do have the latest known version of this point in the channel DB. The following command tries to find all private keys for channels that have been closed by the other party. The command needs to know what channels it is operating on, so we have to supply thesummary-yyy-mm-dd.jsoncreated by the previous command:
chantools --fromsummary ./results/<summary-file-created-in-last-step>.json rescueclosed --channeldb ./results/compacted.db
This will create a new file called./results/rescueclosed-yyyy-mm-dd.jsonwhich will contain any found private keys and will also be needed for the next command. Usebitcoindor Electrum Wallet to sweep all of the private keys. -
chantools forceclose: This command will now close all channels that
chantoolsthinks are still open. This is achieved by publishing the latest known channel state of thechannel.dbfile.
Please read the full warning text of theforceclosecommand below as this command can put your funds at risk if the state in the channel DB is not the most recent one. This command should only be executed for channels where the remote peer is not online anymore.
chantools --fromsummary ./results/<rescueclosed-file-created-in-last-step>.json forceclose --channeldb ./results/compacted.db --publish
This will create a new file called./results/forceclose-yyyy-mm-dd.jsonwhich will be needed for the next command. -
Wait for timelocks: The previous command closed the remaining open channels by publishing your node's state of the channel. By design of the Lightning Network, you now have to wait until the channel funds belonging to you are not time locked any longer. Depending on the size of the channel, you have to wait for somewhere between 144 and 2000 confirmations of the force-close transactions. Only continue with the next step after the channel with the highest
csv_delayhas reached that many confirmations of its closing transaction. You can check this by looking up each force closed channel transaction on a block explorer (like blockstream.info for example). Open the result JSON file of the last command (./results/forceclose-yyyy-mm-dd.json) and look up every TXID in"force_close" -> "txid"on the explorer. If the number of confirmations is equal to or greater to the value shown in"force_close" -> "csv_delay"for each of the channels, you can proceed. -
chantools sweeptimelock: Once all force-close transactions have reached the number of transactions as the
csv_timeoutin the JSON demands, these time locked funds can now be swept. Use the following command to sweep all the channel funds to an address of your wallet:
chantools --fromsummary ./results/<forceclose-file-created-in-last-step>.json sweeptimelock --publish --sweepaddr <bech32-address-from-your-wallet> -
Manual intervention necessary: You got to this step because you either don't have a
channel.dbfile or becausechantoolscouldn't rescue all your node's channels. There are a few things you can try manually that have some chance of working:
- Make sure you can connect to all nodes when restoring from SCB: It happens
all the time that nodes change their IP addresses. When restoring from a
static channel backup, your node tries to connect to the node using the IP
address encoded in the backup file. If the address changed, the SCB restore
process doesn't work. You can use block explorers like 1ml.com
to try to find an IP address that is up-to-date. Just run
lncli connect <node-pubkey>@<updated-ip-address>:<port>in the recoveredlndnode from step 3 and wait a few hours to see if the channel is now being force closed by the remote node. - Find out who the node belongs to: Maybe you opened the channel with someone
you know. Or maybe their node alias contains some information about who the
node belongs to. If you can find out who operates the remote node, you can
ask them to force-close the channel from your end. If the channel was opened
with the
option_static_remote_key, (lnd v0.8.0and later), the funds can be swept by your node.
Seed and passphrase input
All commands that require the seed (and, if set, the seed's passphrase) offer three distinct possibilities to specify it:
- Enter manually on the terminal: This is the safest option as it makes sure that the seed isn't stored in the terminal's command history.
- Pass the extened master root key as parameter: This is added as an option
for users who don't have the full seed anymore, possibly because they used
lnd's--noseedbackupflag and extracted thexprvfrom the wallet database with thewalletinfocommand. Those users can specify the master root key by passing the--rootkeycommand line flag to each command that requires the seed. - Use environment variables: This option makes it easy to automate usage of
chantoolsby removing the need to type into the terminal. There are three environment variables that can be set to skip entering values through the terminal:AEZEED_MNEMONIC: Specifies the 24 wordlndaezeed.AEZEED_PASSPHRASE: Specifies the passphrase for the aezeed. If no passphrase was used during the creation of the seed, the special valueAEZEED_PASSPHRASE="-"needs to be passed to indicate no passphrase should be used or read from the terminal.WALLET_PASSWORD: Specifies the encryption password that is needed to access awallet.dbfile. This is currently only used by thewalletinfocommand.
Example using environment variables:
# We add a space in front of each command to tell bash we don't want this
# command stored in the history.
$ export AEZEED_MNEMONIC="abandon able ... ... ..."
# We didn't set a passphrase for this example seed, we need to indicate this by
# passing in a single dash character.
$ export AEZEED_PASSPHRASE="-"
$ chantools showrootkey
2020-10-29 20:22:42.329 [INF] CHAN: chantools version v0.6.0 commit v0.6.0-3
Your BIP32 HD root key is: xprv9s21ZrQH1...
Command overview
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] <command>
Application Options:
--testnet Set to true if testnet parameters should be used.
--apiurl= API URL to use (must be esplora compatible). (default: https://blockstream.info/api)
--listchannels= The channel input is in the format of lncli's listchannels format. Specify '-' to read from stdin.
--pendingchannels= The channel input is in the format of lncli's pendingchannels format. Specify '-' to read from stdin.
--fromsummary= The channel input is in the format of this tool's channel summary. Specify '-' to read from stdin.
--fromchanneldb= The channel input is in the format of an lnd channel.db file.
Help Options:
-h, --help Show this help message
Available commands:
chanbackup Create a channel.backup file from a channel database.
compactdb Open a source channel.db database file in safe/read-only mode and copy it to a fresh database, compacting it in the process.
derivekey Derive a key with a specific derivation path from the BIP32 HD root key.
dumpbackup Dump the content of a channel.backup file.
dumpchannels Dump all channel information from lnd's channel database.
filterbackup Filter an lnd channel.backup file and remove certain channels.
fixoldbackup Fixes an old channel.backup file that is affected by the lnd issue #3881 (unable to derive shachain root key).
forceclose Force-close the last state that is in the channel.db provided.
genimportscript Generate a script containing the on-chain keys of an lnd wallet that can be imported into other software like bitcoind.
removechannel Remove a single channel from the given channel DB.
rescueclosed Try finding the private keys for funds that are in outputs of remotely force-closed channels.
rescuefunding Rescue funds locked in a funding multisig output that never resulted in a proper channel. This is the command the initiator of the channel needs to run.
showrootkey Extract and show the BIP32 HD root key from the 24 word lnd aezeed.
signrescuefunding Rescue funds locked in a funding multisig output that never resulted in a proper channel. This is the command the remote node (the non-initiator) of the channel needs to run.
summary Compile a summary about the current state of channels.
sweeptimelock Sweep the force-closed state after the time lock has expired.
sweeptimelockmanual Sweep the force-closed state of a single channel manually if only a channel backup file is available
vanitygen Generate a seed with a custom lnd node identity public key that starts with the given prefix.
walletinfo Shows relevant information about an lnd wallet.db file and optionally extracts the BIP32 HD root key.
Commands
chanbackup
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] chanbackup [chanbackup-OPTIONS]
[chanbackup command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key of the wallet that should be used to create the backup. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--channeldb= The lnd channel.db file to create the backup from.
--multi_file= The lnd channel.backup file to create.
This command creates a new channel.backup from a channel.db file.
Example command:
chantools chanbackup --rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--channeldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db \
--multi_file new_channel_backup.backup
compactdb
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] compactdb [compactdb-OPTIONS]
[compactdb command options]
--txmaxsize= Maximum transaction size. (default 65536)
--sourcedb= The lnd channel.db file to create the database backup from.
--destdb= The lnd new channel.db file to copy the compacted database to.
This command opens a database in read-only mode and tries to create a copy of it to a destination file, compacting it in the process.
Example command:
chantools compactdb --sourcedb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db \
--destdb ./results/compacted.db
derivekey
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] derivekey [derivekey-OPTIONS]
[derivekey command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to derive the key from. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--path= The BIP32 derivation path to derive. Must start with "m/".
--neuter Do not output the private key, just the public key.
This command derives a single key with the given BIP32 derivation path from the root key and prints it to the console. Make sure to escape apostrophes in the derivation path.
Example command:
chantools derivekey --rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx --path m/1017\'/0\'/5\'/0/0 \
--neuter
dumpbackup
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] dumpbackup [dumpbackup-OPTIONS]
[dumpbackup command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key of the wallet that was used to create the backup. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--multi_file= The lnd channel.backup file to dump.
This command dumps all information that is inside a channel.backup file in a
human readable format.
Example command:
chantools dumpbackup --rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--multi_file ~/.lnd/data/chain/bitcoin/mainnet/channel.backup
dumpchannels
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] dumpchannels [dumpchannels-OPTIONS]
[dumpchannels command options]
--channeldb= The lnd channel.db file to dump the channels from.
This command dumps all open and pending channels from the given lnd channel.db
file in a human readable format.
Example command:
chantools dumpchannels --channeldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db
filterbackup
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] filterbackup [filterbackup-OPTIONS]
[filterbackup command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key of the wallet that was used to create the backup. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--multi_file= The lnd channel.backup file to filter.
--discard= A comma separated list of channel funding outpoints (format <fundingTXID>:<index>) to remove from the backup file.
Filter an lnd channel.backup file by removing certain channels (identified by
their funding transaction outpoints).
Example command:
chantools filterbackup --rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--multi_file ~/.lnd/data/chain/bitcoin/mainnet/channel.backup \
--discard 2abcdef2b2bffaaa...db0abadd:1,4abcdef2b2bffaaa...db8abadd:0
fixoldbackup
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] fixoldbackup [fixoldbackup-OPTIONS]
[fixoldbackup command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key of the wallet that was used to create the backup. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--multi_file= The lnd channel.backup file to fix.
Fixes an old channel.backup file that is affected by the lnd issue
#3881 ([lncli]
unable to restore chan backups: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = unable
to unpack chan backup: unable to derive shachain root key: unable to derive
private key).
Example command:
chantools fixoldbackup --rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--multi_file ~/.lnd/data/chain/bitcoin/mainnet/channel.backup
forceclose
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] forceclose [forceclose-OPTIONS]
[forceclose command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to use. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--channeldb= The lnd channel.db file to use for force-closing channels.
--publish Should the force-closing TX be published to the chain API?
If you are certain that a node is offline for good (AFTER you've tried SCB!) and a channel is still open, you can use this method to force-close your latest state that you have in your channel.db.
!!! WARNING !!! DANGER !!! WARNING !!!
If you do this and the state that you publish is not the latest state, then the remote node could punish you by taking the whole channel amount if they come online before you can sweep the funds from the time locked (144 - 2000 blocks) transaction or they have a watch tower looking out for them.
This should absolutely be the last resort and you have been warned!
Example command:
chantools --fromsummary results/summary-xxxx-yyyy.json \
forceclose \
--channeldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db \
--rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--publish
genimportscript
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] genimportscript [genimportscript-OPTIONS]
[genimportscript command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to use. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--format= The format of the generated import script. Currently supported are: bitcoin-cli, bitcoin-cli-watchonly, bitcoin-importwallet.
--lndpaths Use all derivation paths that lnd uses. Results in a large number of results. Cannot be used in conjunction with --derivationpath.
--derivationpath= Use one specific derivation path. Specify the first levels of the derivation path before any internal/external branch. Cannot be used in conjunction with --lndpaths. (default m/84'/0'/0')
--recoverywindow= The number of keys to scan per internal/external branch. The output will consist of double this amount of keys. (default 2500)
--rescanfrom= The block number to rescan from. Will be set automatically from the wallet birthday if the lnd 24 word aezeed is entered. (default 500000)
Generates a script that contains all on-chain private (or public) keys derived
from an lnd 24 word aezeed wallet. That script can then be imported into other
software like bitcoind.
The following script formats are currently supported:
bitcoin-cli: Creates a list ofbitcoin-cli importprivkeycommands that can be used in combination with abitcoindfull node to recover the funds locked in those private keys.bitcoin-cli-watchonly: Does the same asbitcoin-clibut with thebitcoin-cli importpubkeycommand. That means, only the public keys are imported intobitcoindto watch the UTXOs of those keys. The funds cannot be spent that way as they are watch-only.bitcoin-importwallet: Creates a text output that is compatible withbitcoind's `importwallet command.
Example command:
chantools genimportscript --format bitcoin-cli --recoverywindow 5000
removechannel
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] removechannel [removechannel-OPTIONS]
[removechannel command options]
--channeldb= The lnd channel.db file to remove the channel from.
--channel= The channel to remove from the DB file, identified by its channel point (<txid>:<txindex>).
Removes a single channel from the given channel DB.
Example command:
chantools --channeldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db \
--channel 3149764effbe82718b280de425277e5e7b245a4573aa4a0203ac12cee1c37816:0
rescueclosed
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] rescueclosed [rescueclosed-OPTIONS]
[rescueclosed command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to use. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--channeldb= The lnd channel.db file to use for rescuing force-closed channels.
If channels have already been force-closed by the remote peer, this command tries to find the private keys to sweep the funds from the output that belongs to our side. This can only be used if we have a channel DB that contains the latest commit point. Normally you would use SCB to get the funds from those channels. But this method can help if the other node doesn't know about the channels any more but we still have the channel.db from the moment they force-closed.
Example command:
chantools --fromsummary results/summary-xxxx-yyyy.json \
rescueclosed \
--channeldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db \
--rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx
rescuefunding
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] rescuefunding [rescuefunding-OPTIONS]
[rescuefunding command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to use. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--channeldb= The lnd channel.db file to rescue a channel from. Must contain the pending channel specified with --channelpoint.
--channelpoint= The funding transaction outpoint of the channel to rescue (<txid>:<txindex>) as it is recorded in the DB.
--confirmedchannelpoint= The channel outpoint that got confirmed on chain (<txid>:<txindex>). Normally this is the same as the --channelpoint so it will be set to that value if this is left empty.
--sweepaddr= The address to sweep the rescued funds to.
--satperbyte= The fee rate to use in satoshis/vByte.
This is part 1 of a two phase process to rescue a channel funding output that was created on chain by accident but never resulted in a proper channel and no commitment transactions exist to spend the funds locked in the 2-of-2 multisig.
You need the cooperation of the channel partner (remote node) for this to
work! They need to run the second command of this process:
signrescuefunding
Example command (run against the channel DB of the initiator node):
chantools rescuefunding \
--channeldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db \
--channelpoint xxxxxxx:xx \
--sweepaddr bc1qxxxxxxxxx \
--satperbyte 10 \
--rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx
If successful, this will create a PSBT that then has to be sent to the channel partner (remote node operator).
showrootkey
This command converts the 24 word lnd aezeed phrase and password to the BIP32
HD root key that is used as the rootkey parameter in other commands of this
tool.
Example command:
chantools showrootkey
signrescuefunding
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] signrescuefunding [signrescuefunding-OPTIONS]
[signrescuefunding command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root (m/) key to derive the key for our part of the signature from.
--psbt= The Partially Signed Bitcoin Transaction that was provided by the initiator of the channel to rescue.
This is part 2 of a two phase process to rescue a channel funding output that was created on chain by accident but never resulted in a proper channel and no commitment transactions exist to spend the funds locked in the 2-of-2 multisig.
Example command (run by the non-initiator of the channel):
chantools signrescuefunding \
--psbt <the_base64_encoded_psbt_from_step_1> \
--rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx
If successful, this will create a final on-chain transaction that can be broadcast by any Bitcoin node.
summary
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] summary
From a list of channels, find out what their state is by querying the funding transaction on a block explorer API.
Example command 1:
lncli listchannels | chantools --listchannels - summary
Example command 2:
chantools --fromchanneldb ~/.lnd/data/graph/mainnet/channel.db
sweeptimelock
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] sweeptimelock [sweeptimelock-OPTIONS]
[sweeptimelock command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to use. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--publish Should the sweep TX be published to the chain API?
--sweepaddr= The address the funds should be sweeped to
--maxcsvlimit= Maximum CSV limit to use. (default 2000)
Use this command to sweep the funds from channels that you force-closed with the
forceclose command. You MUST use the result file that was created with the
forceclose command, otherwise it won't work. You also have to wait until the
highest time lock (can be up to 2000 blocks which is more than two weeks) of all
the channels has passed. If you only want to sweep channels that have the
default CSV limit of 1 day, you can set the --maxcsvlimit parameter to 144.
Example command:
chantools --fromsummary results/forceclose-xxxx-yyyy.json \
sweeptimelock
--rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--publish \
--sweepaddr bc1q.....
sweeptimelockmanual
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] sweeptimelockmanual [sweeptimelockmanual-OPTIONS]
[sweeptimelockmanual command options]
--rootkey= BIP32 HD root key to use. Leave empty to prompt for lnd 24 word aezeed.
--publish Should the sweep TX be published to the chain API?
--sweepaddr= The address the funds should be sweeped to.
--maxcsvlimit= Maximum CSV limit to use. (default 2000)
--feerate= The fee rate to use for the sweep transaction in sat/vByte. (default 2 sat/vByte)
--timelockaddr= The address of the time locked commitment output where the funds are stuck in.
--remoterevbasepoint= The remote's revocation base point, can be found in a channel.backup file.
Sweep the locally force closed state of a single channel manually if only a
channel backup file is available. This can only be used if a channel is force
closed from the local node but then that node's state is lost and only the
channel.backup file is available.
To get the value for --remoterevbasepoint you must use the
dumpbackup command, then look up the value for
RemoteChanCfg -> RevocationBasePoint -> PubKey.
To get the value for --timelockaddr you must look up the channel's funding
output on chain, then follow it to the force close output. The time locked
address is always the one that's longer (because it's P2WSH and not P2PKH).
Example command:
chantools sweeptimelockmanual \
--rootkey xprvxxxxxxxxxx \
--sweepaddr bc1q..... \
--timelockaddr bc1q............ \
--remoterevbasepoint 03xxxxxxx \
--feerate 10 \
--publish
vanitygen
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] vanitygen [vanitygen-OPTIONS]
[vanitygen command options]
--prefix= Hex encoded prefix to find in node public key.
--threads= Number of parallel threads. (default: 4)
Try random lnd compatible seeds until one is found that produces a node identity public key that starts with the given prefix.
Example command:
chantools vanitygen --prefix 022222 --threads 8
Example output:
Running vanitygen on 8 threads. Prefix bit length is 17, expecting to approach
probability p=1.0 after 131,072 seeds.
Tested 185k seeds, p=1.41296, speed=14k/s, elapsed=13s
Looking for 022222, found pubkey: 022222f015540ddde9bdf7c95b24f1d44f7ea6ab69bec83d6fbe622296d64b51d6
with seed: [ability roast pear stomach wink cable tube trumpet shy caught hunt someone border organ spoon only prepare calm silent million tobacco chaos normal phone]
walletinfo
Usage:
chantools [OPTIONS] walletinfo [walletinfo-OPTIONS]
[walletinfo command options]
--walletdb= The lnd wallet.db file to dump the contents from.
--withrootkey Should the BIP32 HD root key of the wallet be printed to standard out?
Shows some basic information about an lnd wallet.db file, like the node
identity the wallet belongs to, how many on-chain addresses are used and, if
enabled with --withrootkey the BIP32 HD root key of the wallet. The latter can
be useful to recover funds from a wallet if the wallet password is still known
but the seed was lost. The 24 word seed phrase itself cannot be extracted
because it is hashed into the extended HD root key before storing it in the
wallet.db.
Example command:
chantools walletinfo \
--walletdb ~/.lnd/data/chain/bitcoin/mainnet/wallet.db \
--withrootkey