* fix ci/cd error * update copyright year * Modify remaining years * solve ci report settings.json code style * update .prettierrc.json * prettierrc fix code style * fix rb file i.to_s and code style * fix error Line is too long. [101/100] * Modify the Ruby file format and restore other file formats * update makefile and readme file space |
7 months ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| .cargo | 3 years ago | |
| .vscode | 7 months ago | |
| kernel | 7 months ago | |
| libraries | 7 months ago | |
| Cargo.lock | 1 year ago | |
| Cargo.toml | 2 years ago | |
| Makefile | 7 months ago | |
| README.md | 7 months ago | |
README.md
Tutorial 14 - Virtual Memory Part 2: MMIO Remap
tl;dr
- We introduce a first set of changes which is eventually needed for separating
kernelanduseraddress spaces. - The memory mapping strategy gets more sophisticated as we do away with
identity mappingthe whole of the board's address space. - Instead, only ranges that are actually needed are mapped:
- The
kernel binarystaysidentity mappedfor now. - Device
MMIO regionsare remapped lazily (to a special reserved virtual address region).
- The
Table of Contents
Introduction
This tutorial is a first step of many needed for enabling userspace applications (which we
hopefully will have some day in the very distant future).
For this, one of the features we want is a clean separation of kernel and user address spaces.
Fortunately, ARMv8 has convenient architecture support to realize this. The following text and
pictue gives some more motivation and technical information. It is quoted from the ARM Cortex-A
Series Programmer’s Guide for ARMv8-A, Chapter 12.2, Separation of kernel and application Virtual
Address spaces:
Operating systems typically have a number of applications or tasks running concurrently. Each of these has its own unique set of translation tables and the kernel switches from one to another as part of the process of switching context between one task and another. However, much of the memory system is used only by the kernel and has fixed virtual to Physical Address mappings where the translation table entries rarely change. The ARMv8 architecture provides a number of features to efficiently handle this requirement.
The table base addresses are specified in the Translation Table Base Registers
TTBR0_EL1andTTBR1_EL1. The translation table pointed to byTTBR0is selected when the upper bits of the VA are all 0.TTBR1is selected when the upper bits of the VA are all set to 1. [...]Figure 12-4 shows how the kernel space can be mapped to the most significant area of memory and the Virtual Address space associated with each application mapped to the least significant area of memory. However, both of these are mapped to a much smaller Physical Address space.
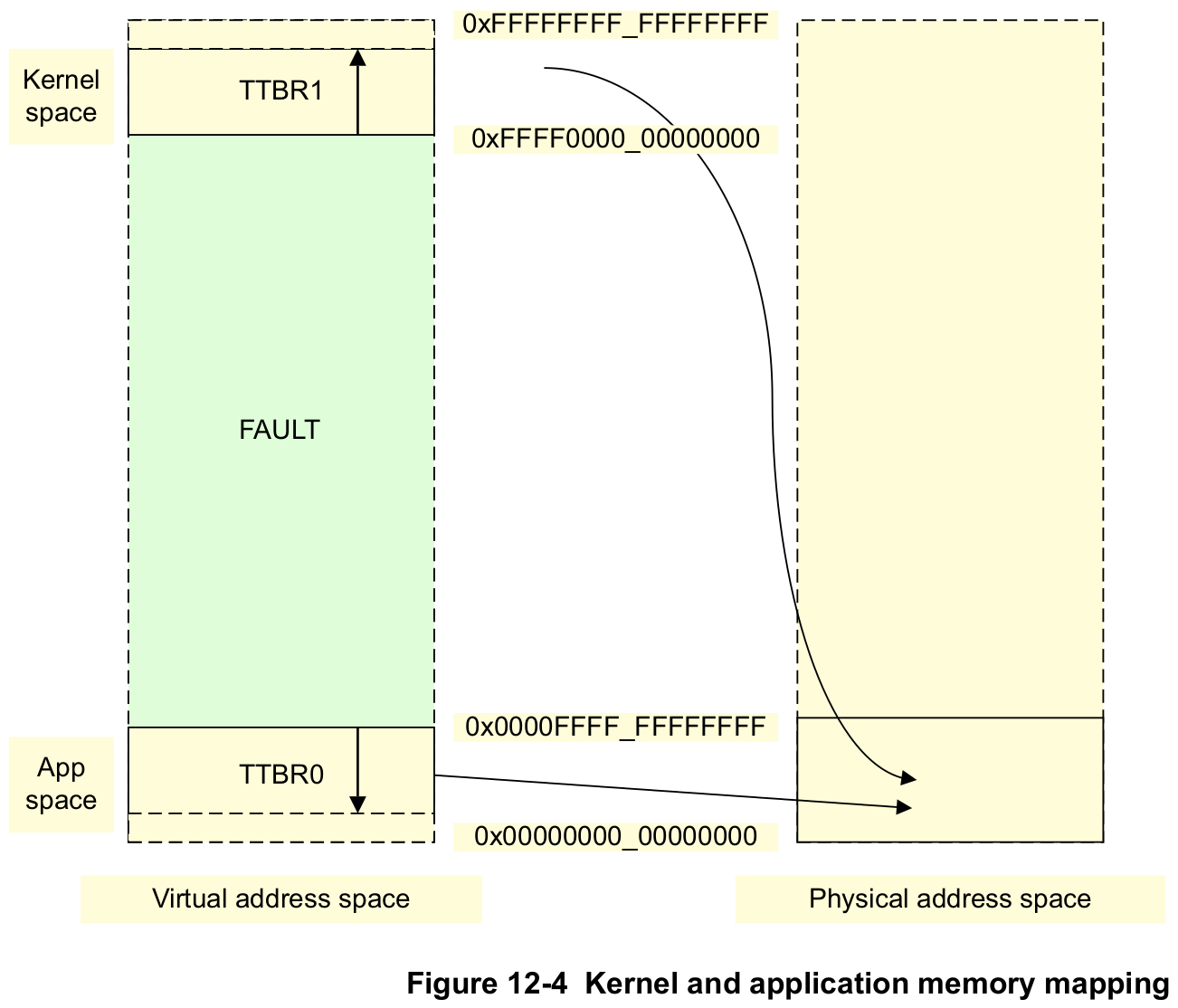
This approach is also sometimes called a "higher half kernel". To eventually achieve this separation, this tutorial makes a start by changing the following things:
- Instead of bulk-
identity mappingthe whole of the board's address space, only the particular parts that are needed will be mapped. - For now, the
kernel binarystays identity mapped. This will be changed in the coming tutorials as it is a quite difficult and peculiar exercise to remap the kernel. - Device
MMIO regionsare lazily remapped during device driver bringup (using the newDriverManagefunctioninstantiate_drivers()).- A dedicated region of virtual addresses that we reserve using
BSPcode and thelinker scriptis used for this.
- A dedicated region of virtual addresses that we reserve using
- We keep using
TTBR0for the kernel translation tables for now. This will be changed when we remap thekernel binaryin the coming tutorials.
Implementation
Until now, the whole address space of the board was identity mapped at once. The architecture
(src/_arch/_/memory/**) and bsp (src/bsp/_/memory/**) parts of the kernel worked
together directly while setting up the translation tables, without any indirection through generic
kernel code (src/memory/**).
The way it worked was that the architectural MMU code would query the bsp code about the start
and end of the physical address space, and any special regions in this space that need a mapping
that is not normal chacheable DRAM. It would then go ahead and map the whole address space at once
and never touch the translation tables again during runtime.
Changing in this tutorial, architecture and bsp code will no longer autonomously create the virtual memory mappings. Instead, this is now orchestrated by the kernel's generic MMU subsystem code.
A New Mapping API in src/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
First, we define an interface for operating on translation tables:
/// Translation table operations.
pub trait TranslationTable {
/// Anything that needs to run before any of the other provided functions can be used.
///
/// # Safety
///
/// - Implementor must ensure that this function can run only once or is harmless if invoked
/// multiple times.
fn init(&mut self);
/// The translation table's base address to be used for programming the MMU.
fn phys_base_address(&self) -> Address<Physical>;
/// Map the given virtual memory region to the given physical memory region.
unsafe fn map_at(
&mut self,
virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
attr: &AttributeFields,
) -> Result<(), &'static str>;
}
In order to enable the generic kernel code to manipulate the kernel's translation tables, they must
first be made accessible. Until now, they were just a "hidden" struct in the architectural MMU
driver (src/arch/.../memory/mmu.rs). This made sense because the MMU driver code was the only code
that needed to be concerned with the table data structure, so having it accessible locally
simplified things.
Since the tables need to be exposed to the rest of the kernel code now, it makes sense to move them
to BSP code. Because ultimately, it is the BSP that is defining the translation table's
properties, such as the size of the virtual address space that the tables need to cover.
They are now defined in the global instances region of src/bsp/.../memory/mmu.rs. To control
access, they are guarded by an InitStateLock.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global instances
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// The kernel translation tables.
static KERNEL_TABLES: InitStateLock<KernelTranslationTable> =
InitStateLock::new(KernelTranslationTable::new());
The struct KernelTranslationTable is a type alias defined in the same file, which in turn gets its
definition from an associated type of type KernelVirtAddrSpace, which itself is a type alias of
memory::mmu::AddressSpace. I know this sounds horribly complicated, but in the end this is just
some layers of const generics whose implementation is scattered between generic and arch code.
This is done to (1) ensure a sane compile-time definition of the translation table struct (by doing
various bounds checks), and (2) to separate concerns between generic MMU code and specializations
that come from the architectural part.
In the end, these tables can be accessed by calling bsp::memory::mmu::kernel_translation_tables():
/// Return a reference to the kernel's translation tables.
pub fn kernel_translation_tables() -> &'static InitStateLock<KernelTranslationTable> {
&KERNEL_TABLES
}
Finally, the generic kernel code (src/memory/mmu.rs) now provides a couple of memory mapping
functions that access and manipulate this instance. They are exported for the rest of the kernel to
use:
/// Raw mapping of a virtual to physical region in the kernel translation tables.
///
/// Prevents mapping into the MMIO range of the tables.
pub unsafe fn kernel_map_at(
name: &'static str,
virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
attr: &AttributeFields,
) -> Result<(), &'static str>;
/// MMIO remapping in the kernel translation tables.
///
/// Typically used by device drivers.
pub unsafe fn kernel_map_mmio(
name: &'static str,
mmio_descriptor: &MMIODescriptor,
) -> Result<Address<Virtual>, &'static str>;
/// Map the kernel's binary. Returns the translation table's base address.
pub unsafe fn kernel_map_binary() -> Result<Address<Physical>, &'static str>;
/// Enable the MMU and data + instruction caching.
pub unsafe fn enable_mmu_and_caching(
phys_tables_base_addr: Address<Physical>,
) -> Result<(), MMUEnableError>;
The new APIs in action
kernel_map_binary() and enable_mmu_and_caching() are used early in kernel_init() to set up
virtual memory:
let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
Err(string) => panic!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string),
Ok(addr) => addr,
};
if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
panic!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
}
Both functions internally use bsp and arch specific code to achieve their goals. For example,
memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() itself wraps around a bsp function of the same name
(bsp::memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary()):
/// Map the kernel binary.
pub unsafe fn kernel_map_binary() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
generic_mmu::kernel_map_at(
"Kernel boot-core stack",
// omitted for brevity.
)?;
generic_mmu::kernel_map_at(
"Kernel code and RO data",
&virt_code_region(),
&kernel_virt_to_phys_region(virt_code_region()),
&AttributeFields {
mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadOnly,
execute_never: false,
},
)?;
generic_mmu::kernel_map_at(
"Kernel data and bss",
// omitted for brevity.
)?;
Ok(())
}
Another user of the new APIs is the driver subsystem. As has been said in the introduction, the
goal is to remap the MMIO regions of the drivers. To achieve this in a seamless way, some changes
to the architecture of the driver subsystem were needed.
Until now, the drivers were static instances which had their MMIO addresses statically set in
the constructor. This was fine, because even if virtual memory was activated, only identity mapping was used, so the hardcoded addresses would be valid with and without the MMU being active.
With remapped MMIO addresses, this is not possible anymore, since the remapping will only happen
at runtime. Therefore, the new approach is to defer the whole instantiation of the drivers until the
remapped addresses are known. To achieve this, in src/bsp/raspberrypi/drivers.rs, the static
driver instances are now wrapped into a MaybeUninit (and are also mut now):
static mut PL011_UART: MaybeUninit<device_driver::PL011Uart> = MaybeUninit::uninit();
static mut GPIO: MaybeUninit<device_driver::GPIO> = MaybeUninit::uninit();
#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi3")]
static mut INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER: MaybeUninit<device_driver::InterruptController> =
MaybeUninit::uninit();
#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi4")]
static mut INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER: MaybeUninit<device_driver::GICv2> = MaybeUninit::uninit();
Accordingly, new dedicated instantiate_xyz() functions have been added, which will be called by
the corresponding driver_xyz() functions. Here is an example for the UART:
/// This must be called only after successful init of the memory subsystem.
unsafe fn instantiate_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
let mmio_descriptor = MMIODescriptor::new(mmio::PL011_UART_START, mmio::PL011_UART_SIZE);
let virt_addr =
memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio(device_driver::PL011Uart::COMPATIBLE, &mmio_descriptor)?;
PL011_UART.write(device_driver::PL011Uart::new(virt_addr));
Ok(())
}
/// Function needs to ensure that driver registration happens only after correct instantiation.
unsafe fn driver_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
instantiate_uart()?;
let uart_descriptor = generic_driver::DeviceDriverDescriptor::new(
PL011_UART.assume_init_ref(),
Some(post_init_uart),
Some(exception::asynchronous::irq_map::PL011_UART),
);
generic_driver::driver_manager().register_driver(uart_descriptor);
Ok(())
}
The code shows that an MMIODescriptor is created first, and then used to remap the MMIO region
using memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio(). This function will be discussed in detail in the next
chapter. What's important for now is that it returns the new Virtual Address of the remapped MMIO
region. The constructor of the UART driver now also expects a virtual address.
Next, a new instance of the PL011Uart driver is created, and written into the PL011_UART global
variable (remember, it is defined as MaybeUninit<device_driver::PL011Uart> = MaybeUninit::uninit()). Meaning, after this line of code, PL011_UART is properly initialized.
Only then, the driver is registered with the kernel and thus becomes accessible for the first time.
This ensures that nobody can use the UART before its memory has been initialized properly.
MMIO Virtual Address Allocation
Getting back to the remapping part, let's peek inside memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio(). We can see
that a virtual address region is obtained from an allocator before remapping:
pub unsafe fn kernel_map_mmio(
name: &'static str,
mmio_descriptor: &MMIODescriptor,
) -> Result<Address<Virtual>, &'static str> {
// omitted
let virt_region =
page_alloc::kernel_mmio_va_allocator().lock(|allocator| allocator.alloc(num_pages))?;
kernel_map_at_unchecked(
name,
&virt_region,
&phys_region,
&AttributeFields {
mem_attributes: MemAttributes::Device,
acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
execute_never: true,
},
)?;
// omitted
}
This allocator is defined and implemented in the added file src/memory/mmu/page_alloc.rs. Like
other parts of the mapping code, its implementation makes use of the newly introduced
PageAddress<ATYPE> and MemoryRegion<ATYPE> types (in
src/memory/mmu/types.rs), but apart from that is rather straight
forward. Therefore, it won't be covered in details here.
The more interesting question is: How does the allocator get to learn which VAs it can use?
This is happening in the following function, which gets called as part of
memory::mmu::post_enable_init(), which in turn gets called in kernel_init() after the MMU has
been turned on.
/// Query the BSP for the reserved virtual addresses for MMIO remapping and initialize the kernel's
/// MMIO VA allocator with it.
fn kernel_init_mmio_va_allocator() {
let region = bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mmio_remap_region();
page_alloc::kernel_mmio_va_allocator().lock(|allocator| allocator.init(region));
}
Again, it is the BSP that provides the information. The BSP itself indirectly gets it from the
linker script. In it, we have defined an 8 MiB region right after the .data segment:
__data_end_exclusive = .;
/***********************************************************************************************
* MMIO Remap Reserved
***********************************************************************************************/
__mmio_remap_start = .;
. += 8 * 1024 * 1024;
__mmio_remap_end_exclusive = .;
ASSERT((. & PAGE_MASK) == 0, "MMIO remap reservation is not page aligned")
The two symbols __mmio_remap_start and __mmio_remap_end_exclusive are used by the BSP to learn
the VA range.
Supporting Changes
There's a couple of changes more not covered in this tutorial text, but the reader should ideally skim through them:
src/memory.rsandsrc/memory/mmu/types.rsintroduce supporting types, likeAddress<ATYPE>,PageAddress<ATYPE>andMemoryRegion<ATYPE>. It is worth reading their implementations.src/memory/mmu/mapping_record.rsprovides the generic kernel code's way of tracking previous memory mappings for use cases such as reusing existing mappings (in case of drivers that have their MMIO ranges in the same64 KiBpage) or printing mappings statistics.
Test it
When you load the kernel, you can now see that the driver's MMIO virtual addresses start right after
the .data section:
Raspberry Pi 3:
$ make chainboot
[...]
Minipush 1.0
[MP] ⏳ Waiting for /dev/ttyUSB0
[MP] ✅ Serial connected
[MP] 🔌 Please power the target now
__ __ _ _ _ _
| \/ (_)_ _ (_) | ___ __ _ __| |
| |\/| | | ' \| | |__/ _ \/ _` / _` |
|_| |_|_|_||_|_|____\___/\__,_\__,_|
Raspberry Pi 3
[ML] Requesting binary
[MP] ⏩ Pushing 65 KiB =========================================🦀 100% 0 KiB/s Time: 00:00:00
[ML] Loaded! Executing the payload now
[ 0.740694] mingo version 0.14.0
[ 0.740902] Booting on: Raspberry Pi 3
[ 0.741357] MMU online:
[ 0.741649] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ 0.743393] Virtual Physical Size Attr Entity
[ 0.745138] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ 0.746883] 0x0000_0000_0000_0000..0x0000_0000_0007_ffff --> 0x00_0000_0000..0x00_0007_ffff | 512 KiB | C RW XN | Kernel boot-core stack
[ 0.748486] 0x0000_0000_0008_0000..0x0000_0000_0008_ffff --> 0x00_0008_0000..0x00_0008_ffff | 64 KiB | C RO X | Kernel code and RO data
[ 0.750099] 0x0000_0000_0009_0000..0x0000_0000_000e_ffff --> 0x00_0009_0000..0x00_000e_ffff | 384 KiB | C RW XN | Kernel data and bss
[ 0.751670] 0x0000_0000_000f_0000..0x0000_0000_000f_ffff --> 0x00_3f20_0000..0x00_3f20_ffff | 64 KiB | Dev RW XN | BCM PL011 UART
[ 0.753187] | BCM GPIO
[ 0.754638] 0x0000_0000_0010_0000..0x0000_0000_0010_ffff --> 0x00_3f00_0000..0x00_3f00_ffff | 64 KiB | Dev RW XN | BCM Interrupt Controller
[ 0.756264] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Raspberry Pi 4:
$ BSP=rpi4 make chainboot
[...]
Minipush 1.0
[MP] ⏳ Waiting for /dev/ttyUSB0
[MP] ✅ Serial connected
[MP] 🔌 Please power the target now
__ __ _ _ _ _
| \/ (_)_ _ (_) | ___ __ _ __| |
| |\/| | | ' \| | |__/ _ \/ _` / _` |
|_| |_|_|_||_|_|____\___/\__,_\__,_|
Raspberry Pi 4
[ML] Requesting binary
[MP] ⏩ Pushing 65 KiB =========================================🦀 100% 0 KiB/s Time: 00:00:00
[ML] Loaded! Executing the payload now
[ 0.736136] mingo version 0.14.0
[ 0.736170] Booting on: Raspberry Pi 4
[ 0.736625] MMU online:
[ 0.736918] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ 0.738662] Virtual Physical Size Attr Entity
[ 0.740406] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ 0.742151] 0x0000_0000_0000_0000..0x0000_0000_0007_ffff --> 0x00_0000_0000..0x00_0007_ffff | 512 KiB | C RW XN | Kernel boot-core stack
[ 0.743754] 0x0000_0000_0008_0000..0x0000_0000_0008_ffff --> 0x00_0008_0000..0x00_0008_ffff | 64 KiB | C RO X | Kernel code and RO data
[ 0.745368] 0x0000_0000_0009_0000..0x0000_0000_000d_ffff --> 0x00_0009_0000..0x00_000d_ffff | 320 KiB | C RW XN | Kernel data and bss
[ 0.746938] 0x0000_0000_000e_0000..0x0000_0000_000e_ffff --> 0x00_fe20_0000..0x00_fe20_ffff | 64 KiB | Dev RW XN | BCM PL011 UART
[ 0.748455] | BCM GPIO
[ 0.749907] 0x0000_0000_000f_0000..0x0000_0000_000f_ffff --> 0x00_ff84_0000..0x00_ff84_ffff | 64 KiB | Dev RW XN | GICv2 GICD
[ 0.751380] | GICV2 GICC
[ 0.752853] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Diff to previous
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/Cargo.toml 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/Cargo.toml
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/Cargo.toml
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/Cargo.toml
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
[package]
name = "mingo"
-version = "0.13.0"
+version = "0.14.0"
authors = ["Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>"]
edition = "2021"
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
@@ -14,10 +14,14 @@
//! crate::memory::mmu::translation_table::arch_translation_table
use crate::{
- bsp, memory,
- memory::mmu::{
- arch_mmu::{Granule512MiB, Granule64KiB},
- AccessPermissions, AttributeFields, MemAttributes,
+ bsp,
+ memory::{
+ self,
+ mmu::{
+ arch_mmu::{Granule512MiB, Granule64KiB},
+ AccessPermissions, AttributeFields, MemAttributes, MemoryRegion, PageAddress,
+ },
+ Address, Physical, Virtual,
},
};
use core::convert;
@@ -121,12 +125,9 @@
}
trait StartAddr {
- fn phys_start_addr_u64(&self) -> u64;
- fn phys_start_addr_usize(&self) -> usize;
+ fn phys_start_addr(&self) -> Address<Physical>;
}
-const NUM_LVL2_TABLES: usize = bsp::memory::mmu::KernelAddrSpace::SIZE >> Granule512MiB::SHIFT;
-
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Public Definitions
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -141,10 +142,10 @@
/// Table descriptors, covering 512 MiB windows.
lvl2: [TableDescriptor; NUM_TABLES],
-}
-/// A translation table type for the kernel space.
-pub type KernelTranslationTable = FixedSizeTranslationTable<NUM_LVL2_TABLES>;
+ /// Have the tables been initialized?
+ initialized: bool,
+}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Private Code
@@ -152,12 +153,8 @@
// The binary is still identity mapped, so we don't need to convert here.
impl<T, const N: usize> StartAddr for [T; N] {
- fn phys_start_addr_u64(&self) -> u64 {
- self as *const T as u64
- }
-
- fn phys_start_addr_usize(&self) -> usize {
- self as *const _ as usize
+ fn phys_start_addr(&self) -> Address<Physical> {
+ Address::new(self as *const _ as usize)
}
}
@@ -170,10 +167,10 @@
}
/// Create an instance pointing to the supplied address.
- pub fn from_next_lvl_table_addr(phys_next_lvl_table_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub fn from_next_lvl_table_addr(phys_next_lvl_table_addr: Address<Physical>) -> Self {
let val = InMemoryRegister::<u64, STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR::Register>::new(0);
- let shifted = phys_next_lvl_table_addr >> Granule64KiB::SHIFT;
+ let shifted = phys_next_lvl_table_addr.as_usize() >> Granule64KiB::SHIFT;
val.write(
STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR::NEXT_LEVEL_TABLE_ADDR_64KiB.val(shifted as u64)
+ STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR::TYPE::Table
@@ -230,12 +227,15 @@
}
/// Create an instance.
- pub fn from_output_addr(phys_output_addr: usize, attribute_fields: &AttributeFields) -> Self {
+ pub fn from_output_page_addr(
+ phys_output_page_addr: PageAddress<Physical>,
+ attribute_fields: &AttributeFields,
+ ) -> Self {
let val = InMemoryRegister::<u64, STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::Register>::new(0);
- let shifted = phys_output_addr as u64 >> Granule64KiB::SHIFT;
+ let shifted = phys_output_page_addr.into_inner().as_usize() >> Granule64KiB::SHIFT;
val.write(
- STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::OUTPUT_ADDR_64KiB.val(shifted)
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::OUTPUT_ADDR_64KiB.val(shifted as u64)
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::AF::True
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::TYPE::Page
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::VALID::True
@@ -244,50 +244,133 @@
Self { value: val.get() }
}
+
+ /// Returns the valid bit.
+ fn is_valid(&self) -> bool {
+ InMemoryRegister::<u64, STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::Register>::new(self.value)
+ .is_set(STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::VALID)
+ }
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Public Code
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+impl<const AS_SIZE: usize> memory::mmu::AssociatedTranslationTable
+ for memory::mmu::AddressSpace<AS_SIZE>
+where
+ [u8; Self::SIZE >> Granule512MiB::SHIFT]: Sized,
+{
+ type TableStartFromBottom = FixedSizeTranslationTable<{ Self::SIZE >> Granule512MiB::SHIFT }>;
+}
+
impl<const NUM_TABLES: usize> FixedSizeTranslationTable<NUM_TABLES> {
/// Create an instance.
+ #[allow(clippy::assertions_on_constants)]
pub const fn new() -> Self {
+ assert!(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE == Granule64KiB::SIZE);
+
// Can't have a zero-sized address space.
assert!(NUM_TABLES > 0);
Self {
lvl3: [[PageDescriptor::new_zeroed(); 8192]; NUM_TABLES],
lvl2: [TableDescriptor::new_zeroed(); NUM_TABLES],
+ initialized: false,
}
}
- /// Iterates over all static translation table entries and fills them at once.
- ///
- /// # Safety
- ///
- /// - Modifies a `static mut`. Ensure it only happens from here.
- pub unsafe fn populate_tt_entries(&mut self) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
- for (l2_nr, l2_entry) in self.lvl2.iter_mut().enumerate() {
- *l2_entry =
- TableDescriptor::from_next_lvl_table_addr(self.lvl3[l2_nr].phys_start_addr_usize());
+ /// Helper to calculate the lvl2 and lvl3 indices from an address.
+ #[inline(always)]
+ fn lvl2_lvl3_index_from_page_addr(
+ &self,
+ virt_page_addr: PageAddress<Virtual>,
+ ) -> Result<(usize, usize), &'static str> {
+ let addr = virt_page_addr.into_inner().as_usize();
+ let lvl2_index = addr >> Granule512MiB::SHIFT;
+ let lvl3_index = (addr & Granule512MiB::MASK) >> Granule64KiB::SHIFT;
- for (l3_nr, l3_entry) in self.lvl3[l2_nr].iter_mut().enumerate() {
- let virt_addr = (l2_nr << Granule512MiB::SHIFT) + (l3_nr << Granule64KiB::SHIFT);
+ if lvl2_index > (NUM_TABLES - 1) {
+ return Err("Virtual page is out of bounds of translation table");
+ }
- let (phys_output_addr, attribute_fields) =
- bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout().virt_addr_properties(virt_addr)?;
+ Ok((lvl2_index, lvl3_index))
+ }
- *l3_entry = PageDescriptor::from_output_addr(phys_output_addr, &attribute_fields);
- }
+ /// Sets the PageDescriptor corresponding to the supplied page address.
+ ///
+ /// Doesn't allow overriding an already valid page.
+ #[inline(always)]
+ fn set_page_descriptor_from_page_addr(
+ &mut self,
+ virt_page_addr: PageAddress<Virtual>,
+ new_desc: &PageDescriptor,
+ ) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let (lvl2_index, lvl3_index) = self.lvl2_lvl3_index_from_page_addr(virt_page_addr)?;
+ let desc = &mut self.lvl3[lvl2_index][lvl3_index];
+
+ if desc.is_valid() {
+ return Err("Virtual page is already mapped");
}
+ *desc = *new_desc;
Ok(())
}
+}
- /// The translation table's base address to be used for programming the MMU.
- pub fn phys_base_address(&self) -> u64 {
- self.lvl2.phys_start_addr_u64()
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// OS Interface Code
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl<const NUM_TABLES: usize> memory::mmu::translation_table::interface::TranslationTable
+ for FixedSizeTranslationTable<NUM_TABLES>
+{
+ fn init(&mut self) {
+ if self.initialized {
+ return;
+ }
+
+ // Populate the l2 entries.
+ for (lvl2_nr, lvl2_entry) in self.lvl2.iter_mut().enumerate() {
+ let phys_table_addr = self.lvl3[lvl2_nr].phys_start_addr();
+
+ let new_desc = TableDescriptor::from_next_lvl_table_addr(phys_table_addr);
+ *lvl2_entry = new_desc;
+ }
+
+ self.initialized = true;
+ }
+
+ fn phys_base_address(&self) -> Address<Physical> {
+ self.lvl2.phys_start_addr()
+ }
+
+ unsafe fn map_at(
+ &mut self,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+ ) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ assert!(self.initialized, "Translation tables not initialized");
+
+ if virt_region.size() != phys_region.size() {
+ return Err("Tried to map memory regions with unequal sizes");
+ }
+
+ if phys_region.end_exclusive_page_addr() > bsp::memory::phys_addr_space_end_exclusive_addr()
+ {
+ return Err("Tried to map outside of physical address space");
+ }
+
+ let iter = phys_region.into_iter().zip(virt_region.into_iter());
+ for (phys_page_addr, virt_page_addr) in iter {
+ let new_desc = PageDescriptor::from_output_page_addr(phys_page_addr, attr);
+ let virt_page = virt_page_addr;
+
+ self.set_page_descriptor_from_page_addr(virt_page, &new_desc)?;
+ }
+
+ Ok(())
}
}
@@ -296,6 +379,9 @@
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#[cfg(test)]
+pub type MinSizeTranslationTable = FixedSizeTranslationTable<1>;
+
+#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::*;
use test_macros::kernel_test;
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@
use crate::{
bsp, memory,
- memory::mmu::{translation_table::KernelTranslationTable, TranslationGranule},
+ memory::{mmu::TranslationGranule, Address, Physical},
};
use aarch64_cpu::{asm::barrier, registers::*};
use core::intrinsics::unlikely;
@@ -46,13 +46,6 @@
// Global instances
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-/// The kernel translation tables.
-///
-/// # Safety
-///
-/// - Supposed to land in `.bss`. Therefore, ensure that all initial member values boil down to "0".
-static mut KERNEL_TABLES: KernelTranslationTable = KernelTranslationTable::new();
-
static MMU: MemoryManagementUnit = MemoryManagementUnit;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -87,7 +80,7 @@
/// Configure various settings of stage 1 of the EL1 translation regime.
fn configure_translation_control(&self) {
- let t0sz = (64 - bsp::memory::mmu::KernelAddrSpace::SIZE_SHIFT) as u64;
+ let t0sz = (64 - bsp::memory::mmu::KernelVirtAddrSpace::SIZE_SHIFT) as u64;
TCR_EL1.write(
TCR_EL1::TBI0::Used
@@ -119,7 +112,10 @@
use memory::mmu::MMUEnableError;
impl memory::mmu::interface::MMU for MemoryManagementUnit {
- unsafe fn enable_mmu_and_caching(&self) -> Result<(), MMUEnableError> {
+ unsafe fn enable_mmu_and_caching(
+ &self,
+ phys_tables_base_addr: Address<Physical>,
+ ) -> Result<(), MMUEnableError> {
if unlikely(self.is_enabled()) {
return Err(MMUEnableError::AlreadyEnabled);
}
@@ -134,13 +130,8 @@
// Prepare the memory attribute indirection register.
self.set_up_mair();
- // Populate translation tables.
- KERNEL_TABLES
- .populate_tt_entries()
- .map_err(MMUEnableError::Other)?;
-
// Set the "Translation Table Base Register".
- TTBR0_EL1.set_baddr(KERNEL_TABLES.phys_base_address());
+ TTBR0_EL1.set_baddr(phys_tables_base_addr.as_usize() as u64);
self.configure_translation_control();
@@ -163,33 +154,3 @@
SCTLR_EL1.matches_all(SCTLR_EL1::M::Enable)
}
}
-
-//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-// Testing
-//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-#[cfg(test)]
-mod tests {
- use super::*;
- use core::{cell::UnsafeCell, ops::Range};
- use test_macros::kernel_test;
-
- /// Check if KERNEL_TABLES is in .bss.
- #[kernel_test]
- fn kernel_tables_in_bss() {
- extern "Rust" {
- static __bss_start: UnsafeCell<u64>;
- static __bss_end_exclusive: UnsafeCell<u64>;
- }
-
- let bss_range = unsafe {
- Range {
- start: __bss_start.get(),
- end: __bss_end_exclusive.get(),
- }
- };
- let kernel_tables_addr = unsafe { &KERNEL_TABLES as *const _ as usize as *mut u64 };
-
- assert!(bss_range.contains(&kernel_tables_addr));
- }
-}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicc.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicc.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicc.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicc.rs
@@ -4,7 +4,11 @@
//! GICC Driver - GIC CPU interface.
-use crate::{bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper, exception};
+use crate::{
+ bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper,
+ exception,
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
+};
use tock_registers::{
interfaces::{Readable, Writeable},
register_bitfields, register_structs,
@@ -73,7 +77,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
registers: Registers::new(mmio_start_addr),
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicd.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicd.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicd.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2/gicd.rs
@@ -8,7 +8,9 @@
//! - SPI - Shared Peripheral Interrupt.
use crate::{
- bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper, state, synchronization,
+ bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper,
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
+ state, synchronization,
synchronization::IRQSafeNullLock,
};
use tock_registers::{
@@ -128,7 +130,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
shared_registers: IRQSafeNullLock::new(SharedRegisters::new(mmio_start_addr)),
banked_registers: BankedRegisters::new(mmio_start_addr),
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/arm/gicv2.rs
@@ -81,7 +81,9 @@
use crate::{
bsp::{self, device_driver::common::BoundedUsize},
- cpu, driver, exception, synchronization,
+ cpu, driver, exception,
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
+ synchronization,
synchronization::InitStateLock,
};
@@ -125,7 +127,10 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(gicd_mmio_start_addr: usize, gicc_mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(
+ gicd_mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>,
+ gicc_mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>,
+ ) -> Self {
Self {
gicd: gicd::GICD::new(gicd_mmio_start_addr),
gicc: gicc::GICC::new(gicc_mmio_start_addr),
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_gpio.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_gpio.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_gpio.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_gpio.rs
@@ -5,8 +5,12 @@
//! GPIO Driver.
use crate::{
- bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper, driver, exception::asynchronous::IRQNumber,
- synchronization, synchronization::IRQSafeNullLock,
+ bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper,
+ driver,
+ exception::asynchronous::IRQNumber,
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
+ synchronization,
+ synchronization::IRQSafeNullLock,
};
use tock_registers::{
interfaces::{ReadWriteable, Writeable},
@@ -131,7 +135,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
registers: Registers::new(mmio_start_addr),
}
@@ -198,7 +202,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
inner: IRQSafeNullLock::new(GPIOInner::new(mmio_start_addr)),
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller/peripheral_ic.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller/peripheral_ic.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller/peripheral_ic.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller/peripheral_ic.rs
@@ -11,7 +11,9 @@
use super::{PendingIRQs, PeripheralIRQ};
use crate::{
bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper,
- exception, synchronization,
+ exception,
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
+ synchronization,
synchronization::{IRQSafeNullLock, InitStateLock},
};
use tock_registers::{
@@ -79,7 +81,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
wo_registers: IRQSafeNullLock::new(WriteOnlyRegisters::new(mmio_start_addr)),
ro_registers: ReadOnlyRegisters::new(mmio_start_addr),
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_interrupt_controller.rs
@@ -10,6 +10,7 @@
bsp::device_driver::common::BoundedUsize,
driver,
exception::{self, asynchronous::IRQHandlerDescriptor},
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
};
use core::fmt;
@@ -91,7 +92,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(periph_mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(periph_mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
periph: peripheral_ic::PeripheralIC::new(periph_mmio_start_addr),
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_pl011_uart.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_pl011_uart.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_pl011_uart.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/bcm/bcm2xxx_pl011_uart.rs
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@
bsp::device_driver::common::MMIODerefWrapper,
console, cpu, driver,
exception::{self, asynchronous::IRQNumber},
+ memory::{Address, Virtual},
synchronization,
synchronization::IRQSafeNullLock,
};
@@ -244,7 +245,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
registers: Registers::new(mmio_start_addr),
chars_written: 0,
@@ -395,7 +396,7 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - The user must ensure to provide a correct MMIO start address.
- pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(mmio_start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
inner: IRQSafeNullLock::new(PL011UartInner::new(mmio_start_addr)),
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/common.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/common.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/common.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/device_driver/common.rs
@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@
//! Common device driver code.
+use crate::memory::{Address, Virtual};
use core::{fmt, marker::PhantomData, ops};
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -11,7 +12,7 @@
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pub struct MMIODerefWrapper<T> {
- start_addr: usize,
+ start_addr: Address<Virtual>,
phantom: PhantomData<fn() -> T>,
}
@@ -25,7 +26,7 @@
impl<T> MMIODerefWrapper<T> {
/// Create an instance.
- pub const unsafe fn new(start_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ pub const unsafe fn new(start_addr: Address<Virtual>) -> Self {
Self {
start_addr,
phantom: PhantomData,
@@ -37,7 +38,7 @@
type Target = T;
fn deref(&self) -> &Self::Target {
- unsafe { &*(self.start_addr as *const _) }
+ unsafe { &*(self.start_addr.as_usize() as *const _) }
}
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/driver.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/driver.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/driver.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/driver.rs
@@ -9,52 +9,109 @@
bsp::device_driver,
console, driver as generic_driver,
exception::{self as generic_exception},
+ memory,
+ memory::mmu::MMIODescriptor,
+};
+use core::{
+ mem::MaybeUninit,
+ sync::atomic::{AtomicBool, Ordering},
};
-use core::sync::atomic::{AtomicBool, Ordering};
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global instances
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-static PL011_UART: device_driver::PL011Uart =
- unsafe { device_driver::PL011Uart::new(mmio::PL011_UART_START) };
-static GPIO: device_driver::GPIO = unsafe { device_driver::GPIO::new(mmio::GPIO_START) };
+static mut PL011_UART: MaybeUninit<device_driver::PL011Uart> = MaybeUninit::uninit();
+static mut GPIO: MaybeUninit<device_driver::GPIO> = MaybeUninit::uninit();
#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi3")]
-static INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER: device_driver::InterruptController =
- unsafe { device_driver::InterruptController::new(mmio::PERIPHERAL_IC_START) };
+static mut INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER: MaybeUninit<device_driver::InterruptController> =
+ MaybeUninit::uninit();
#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi4")]
-static INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER: device_driver::GICv2 =
- unsafe { device_driver::GICv2::new(mmio::GICD_START, mmio::GICC_START) };
+static mut INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER: MaybeUninit<device_driver::GICv2> = MaybeUninit::uninit();
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Private Code
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+/// This must be called only after successful init of the memory subsystem.
+unsafe fn instantiate_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let mmio_descriptor = MMIODescriptor::new(mmio::PL011_UART_START, mmio::PL011_UART_SIZE);
+ let virt_addr =
+ memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio(device_driver::PL011Uart::COMPATIBLE, &mmio_descriptor)?;
+
+ PL011_UART.write(device_driver::PL011Uart::new(virt_addr));
+
+ Ok(())
+}
+
/// This must be called only after successful init of the UART driver.
-fn post_init_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
- console::register_console(&PL011_UART);
+unsafe fn post_init_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ console::register_console(PL011_UART.assume_init_ref());
+
+ Ok(())
+}
+
+/// This must be called only after successful init of the memory subsystem.
+unsafe fn instantiate_gpio() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let mmio_descriptor = MMIODescriptor::new(mmio::GPIO_START, mmio::GPIO_SIZE);
+ let virt_addr =
+ memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio(device_driver::GPIO::COMPATIBLE, &mmio_descriptor)?;
+
+ GPIO.write(device_driver::GPIO::new(virt_addr));
Ok(())
}
/// This must be called only after successful init of the GPIO driver.
-fn post_init_gpio() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
- GPIO.map_pl011_uart();
+unsafe fn post_init_gpio() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ GPIO.assume_init_ref().map_pl011_uart();
+ Ok(())
+}
+
+/// This must be called only after successful init of the memory subsystem.
+#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi3")]
+unsafe fn instantiate_interrupt_controller() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let periph_mmio_descriptor =
+ MMIODescriptor::new(mmio::PERIPHERAL_IC_START, mmio::PERIPHERAL_IC_SIZE);
+ let periph_virt_addr = memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio(
+ device_driver::InterruptController::COMPATIBLE,
+ &periph_mmio_descriptor,
+ )?;
+
+ INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER.write(device_driver::InterruptController::new(periph_virt_addr));
+
+ Ok(())
+}
+
+/// This must be called only after successful init of the memory subsystem.
+#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi4")]
+unsafe fn instantiate_interrupt_controller() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let gicd_mmio_descriptor = MMIODescriptor::new(mmio::GICD_START, mmio::GICD_SIZE);
+ let gicd_virt_addr = memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio("GICv2 GICD", &gicd_mmio_descriptor)?;
+
+ let gicc_mmio_descriptor = MMIODescriptor::new(mmio::GICC_START, mmio::GICC_SIZE);
+ let gicc_virt_addr = memory::mmu::kernel_map_mmio("GICV2 GICC", &gicc_mmio_descriptor)?;
+
+ INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER.write(device_driver::GICv2::new(gicd_virt_addr, gicc_virt_addr));
+
Ok(())
}
/// This must be called only after successful init of the interrupt controller driver.
-fn post_init_interrupt_controller() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
- generic_exception::asynchronous::register_irq_manager(&INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER);
+unsafe fn post_init_interrupt_controller() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ generic_exception::asynchronous::register_irq_manager(INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER.assume_init_ref());
Ok(())
}
-fn driver_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+/// Function needs to ensure that driver registration happens only after correct instantiation.
+unsafe fn driver_uart() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ instantiate_uart()?;
+
let uart_descriptor = generic_driver::DeviceDriverDescriptor::new(
- &PL011_UART,
+ PL011_UART.assume_init_ref(),
Some(post_init_uart),
Some(exception::asynchronous::irq_map::PL011_UART),
);
@@ -63,17 +120,26 @@
Ok(())
}
-fn driver_gpio() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
- let gpio_descriptor =
- generic_driver::DeviceDriverDescriptor::new(&GPIO, Some(post_init_gpio), None);
+/// Function needs to ensure that driver registration happens only after correct instantiation.
+unsafe fn driver_gpio() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ instantiate_gpio()?;
+
+ let gpio_descriptor = generic_driver::DeviceDriverDescriptor::new(
+ GPIO.assume_init_ref(),
+ Some(post_init_gpio),
+ None,
+ );
generic_driver::driver_manager().register_driver(gpio_descriptor);
Ok(())
}
-fn driver_interrupt_controller() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+/// Function needs to ensure that driver registration happens only after correct instantiation.
+unsafe fn driver_interrupt_controller() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ instantiate_interrupt_controller()?;
+
let interrupt_controller_descriptor = generic_driver::DeviceDriverDescriptor::new(
- &INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER,
+ INTERRUPT_CONTROLLER.assume_init_ref(),
Some(post_init_interrupt_controller),
None,
);
@@ -109,5 +175,10 @@
/// than on real hardware due to QEMU's abstractions.
#[cfg(feature = "test_build")]
pub fn qemu_bring_up_console() {
- console::register_console(&PL011_UART);
+ use crate::cpu;
+
+ unsafe {
+ instantiate_uart().unwrap_or_else(|_| cpu::qemu_exit_failure());
+ console::register_console(PL011_UART.assume_init_ref());
+ };
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/kernel.ld 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/kernel.ld
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/kernel.ld
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/kernel.ld
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@
***********************************************************************************************/
.boot_core_stack (NOLOAD) :
{
- /* ^ */
+ __boot_core_stack_start = .; /* ^ */
/* | stack */
. += __rpi_phys_binary_load_addr; /* | growth */
/* | direction */
@@ -67,6 +67,7 @@
/***********************************************************************************************
* Data + BSS
***********************************************************************************************/
+ __data_start = .;
.data : { *(.data*) } :segment_data
/* Section is zeroed in pairs of u64. Align start and end to 16 bytes */
@@ -78,6 +79,18 @@
__bss_end_exclusive = .;
} :segment_data
+ . = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
+ __data_end_exclusive = .;
+
+ /***********************************************************************************************
+ * MMIO Remap Reserved
+ ***********************************************************************************************/
+ __mmio_remap_start = .;
+ . += 8 * 1024 * 1024;
+ __mmio_remap_end_exclusive = .;
+
+ ASSERT((. & PAGE_MASK) == 0, "MMIO remap reservation is not page aligned")
+
/***********************************************************************************************
* Misc
***********************************************************************************************/
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
@@ -4,70 +4,163 @@
//! BSP Memory Management Unit.
-use super::map as memory_map;
-use crate::memory::mmu::*;
-use core::ops::RangeInclusive;
+use crate::{
+ memory::{
+ mmu::{
+ self as generic_mmu, AccessPermissions, AddressSpace, AssociatedTranslationTable,
+ AttributeFields, MemAttributes, MemoryRegion, PageAddress, TranslationGranule,
+ },
+ Physical, Virtual,
+ },
+ synchronization::InitStateLock,
+};
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Private Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+type KernelTranslationTable =
+ <KernelVirtAddrSpace as AssociatedTranslationTable>::TableStartFromBottom;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Public Definitions
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-/// The kernel's address space defined by this BSP.
-pub type KernelAddrSpace = AddressSpace<{ memory_map::END_INCLUSIVE + 1 }>;
+/// The translation granule chosen by this BSP. This will be used everywhere else in the kernel to
+/// derive respective data structures and their sizes. For example, the `crate::memory::mmu::Page`.
+pub type KernelGranule = TranslationGranule<{ 64 * 1024 }>;
+
+/// The kernel's virtual address space defined by this BSP.
+pub type KernelVirtAddrSpace = AddressSpace<{ 1024 * 1024 * 1024 }>;
-const NUM_MEM_RANGES: usize = 2;
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Global instances
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-/// The virtual memory layout.
+/// The kernel translation tables.
///
-/// The layout must contain only special ranges, aka anything that is _not_ normal cacheable DRAM.
-/// It is agnostic of the paging granularity that the architecture's MMU will use.
-pub static LAYOUT: KernelVirtualLayout<NUM_MEM_RANGES> = KernelVirtualLayout::new(
- memory_map::END_INCLUSIVE,
- [
- TranslationDescriptor {
- name: "Kernel code and RO data",
- virtual_range: code_range_inclusive,
- physical_range_translation: Translation::Identity,
- attribute_fields: AttributeFields {
- mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
- acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadOnly,
- execute_never: false,
- },
- },
- TranslationDescriptor {
- name: "Device MMIO",
- virtual_range: mmio_range_inclusive,
- physical_range_translation: Translation::Identity,
- attribute_fields: AttributeFields {
- mem_attributes: MemAttributes::Device,
- acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
- execute_never: true,
- },
- },
- ],
-);
+/// It is mandatory that InitStateLock is transparent.
+///
+/// That is, `size_of(InitStateLock<KernelTranslationTable>) == size_of(KernelTranslationTable)`.
+/// There is a unit tests that checks this porperty.
+static KERNEL_TABLES: InitStateLock<KernelTranslationTable> =
+ InitStateLock::new(KernelTranslationTable::new());
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Private Code
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-fn code_range_inclusive() -> RangeInclusive<usize> {
- // Notice the subtraction to turn the exclusive end into an inclusive end.
- #[allow(clippy::range_minus_one)]
- RangeInclusive::new(super::code_start(), super::code_end_exclusive() - 1)
+/// Helper function for calculating the number of pages the given parameter spans.
+const fn size_to_num_pages(size: usize) -> usize {
+ assert!(size > 0);
+ assert!(size modulo KernelGranule::SIZE == 0);
+
+ size >> KernelGranule::SHIFT
+}
+
+/// The code pages of the kernel binary.
+fn virt_code_region() -> MemoryRegion<Virtual> {
+ let num_pages = size_to_num_pages(super::code_size());
+
+ let start_page_addr = super::virt_code_start();
+ let end_exclusive_page_addr = start_page_addr.checked_offset(num_pages as isize).unwrap();
+
+ MemoryRegion::new(start_page_addr, end_exclusive_page_addr)
+}
+
+/// The data pages of the kernel binary.
+fn virt_data_region() -> MemoryRegion<Virtual> {
+ let num_pages = size_to_num_pages(super::data_size());
+
+ let start_page_addr = super::virt_data_start();
+ let end_exclusive_page_addr = start_page_addr.checked_offset(num_pages as isize).unwrap();
+
+ MemoryRegion::new(start_page_addr, end_exclusive_page_addr)
+}
+
+/// The boot core stack pages.
+fn virt_boot_core_stack_region() -> MemoryRegion<Virtual> {
+ let num_pages = size_to_num_pages(super::boot_core_stack_size());
+
+ let start_page_addr = super::virt_boot_core_stack_start();
+ let end_exclusive_page_addr = start_page_addr.checked_offset(num_pages as isize).unwrap();
+
+ MemoryRegion::new(start_page_addr, end_exclusive_page_addr)
}
-fn mmio_range_inclusive() -> RangeInclusive<usize> {
- RangeInclusive::new(memory_map::mmio::START, memory_map::mmio::END_INCLUSIVE)
+// The binary is still identity mapped, so use this trivial conversion function for mapping below.
+
+fn kernel_virt_to_phys_region(virt_region: MemoryRegion<Virtual>) -> MemoryRegion<Physical> {
+ MemoryRegion::new(
+ PageAddress::from(virt_region.start_page_addr().into_inner().as_usize()),
+ PageAddress::from(
+ virt_region
+ .end_exclusive_page_addr()
+ .into_inner()
+ .as_usize(),
+ ),
+ )
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Public Code
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-/// Return a reference to the virtual memory layout.
-pub fn virt_mem_layout() -> &'static KernelVirtualLayout<NUM_MEM_RANGES> {
- &LAYOUT
+/// Return a reference to the kernel's translation tables.
+pub fn kernel_translation_tables() -> &'static InitStateLock<KernelTranslationTable> {
+ &KERNEL_TABLES
+}
+
+/// The MMIO remap pages.
+pub fn virt_mmio_remap_region() -> MemoryRegion<Virtual> {
+ let num_pages = size_to_num_pages(super::mmio_remap_size());
+
+ let start_page_addr = super::virt_mmio_remap_start();
+ let end_exclusive_page_addr = start_page_addr.checked_offset(num_pages as isize).unwrap();
+
+ MemoryRegion::new(start_page_addr, end_exclusive_page_addr)
+}
+
+/// Map the kernel binary.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Any miscalculation or attribute error will likely be fatal. Needs careful manual checking.
+pub unsafe fn kernel_map_binary() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ generic_mmu::kernel_map_at(
+ "Kernel boot-core stack",
+ &virt_boot_core_stack_region(),
+ &kernel_virt_to_phys_region(virt_boot_core_stack_region()),
+ &AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ },
+ )?;
+
+ generic_mmu::kernel_map_at(
+ "Kernel code and RO data",
+ &virt_code_region(),
+ &kernel_virt_to_phys_region(virt_code_region()),
+ &AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadOnly,
+ execute_never: false,
+ },
+ )?;
+
+ generic_mmu::kernel_map_at(
+ "Kernel data and bss",
+ &virt_data_region(),
+ &kernel_virt_to_phys_region(virt_data_region()),
+ &AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ },
+ )?;
+
+ Ok(())
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -77,38 +170,60 @@
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::*;
+ use core::{cell::UnsafeCell, ops::Range};
use test_macros::kernel_test;
/// Check alignment of the kernel's virtual memory layout sections.
#[kernel_test]
fn virt_mem_layout_sections_are_64KiB_aligned() {
- const SIXTYFOUR_KIB: usize = 65536;
-
- for i in LAYOUT.inner().iter() {
- let start: usize = *(i.virtual_range)().start();
- let end: usize = *(i.virtual_range)().end() + 1;
-
- assert_eq!(start modulo SIXTYFOUR_KIB, 0);
- assert_eq!(end modulo SIXTYFOUR_KIB, 0);
- assert!(end >= start);
+ for i in [
+ virt_boot_core_stack_region,
+ virt_code_region,
+ virt_data_region,
+ ]
+ .iter()
+ {
+ let start = i().start_page_addr().into_inner();
+ let end_exclusive = i().end_exclusive_page_addr().into_inner();
+
+ assert!(start.is_page_aligned());
+ assert!(end_exclusive.is_page_aligned());
+ assert!(end_exclusive >= start);
}
}
/// Ensure the kernel's virtual memory layout is free of overlaps.
#[kernel_test]
fn virt_mem_layout_has_no_overlaps() {
- let layout = virt_mem_layout().inner();
-
- for (i, first) in layout.iter().enumerate() {
- for second in layout.iter().skip(i + 1) {
- let first_range = first.virtual_range;
- let second_range = second.virtual_range;
-
- assert!(!first_range().contains(second_range().start()));
- assert!(!first_range().contains(second_range().end()));
- assert!(!second_range().contains(first_range().start()));
- assert!(!second_range().contains(first_range().end()));
+ let layout = [
+ virt_boot_core_stack_region(),
+ virt_code_region(),
+ virt_data_region(),
+ ];
+
+ for (i, first_range) in layout.iter().enumerate() {
+ for second_range in layout.iter().skip(i + 1) {
+ assert!(!first_range.overlaps(second_range))
}
}
}
+
+ /// Check if KERNEL_TABLES is in .bss.
+ #[kernel_test]
+ fn kernel_tables_in_bss() {
+ extern "Rust" {
+ static __bss_start: UnsafeCell<u64>;
+ static __bss_end_exclusive: UnsafeCell<u64>;
+ }
+
+ let bss_range = unsafe {
+ Range {
+ start: __bss_start.get(),
+ end: __bss_end_exclusive.get(),
+ }
+ };
+ let kernel_tables_addr = &KERNEL_TABLES as *const _ as usize as *mut u64;
+
+ assert!(bss_range.contains(&kernel_tables_addr));
+ }
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs
@@ -10,27 +10,59 @@
//! as the boot core's stack.
//!
//! +---------------------------------------+
-//! | | 0x0
+//! | | boot_core_stack_start @ 0x0
//! | | ^
//! | Boot-core Stack | | stack
//! | | | growth
//! | | | direction
//! +---------------------------------------+
-//! | | code_start @ 0x8_0000
+//! | | code_start @ 0x8_0000 == boot_core_stack_end_exclusive
//! | .text |
//! | .rodata |
//! | .got |
//! | |
//! +---------------------------------------+
-//! | | code_end_exclusive
+//! | | data_start == code_end_exclusive
//! | .data |
//! | .bss |
//! | |
//! +---------------------------------------+
+//! | | data_end_exclusive
//! | |
+//!
+//!
+//!
+//!
+//!
+//! The virtual memory layout is as follows:
+//!
+//! +---------------------------------------+
+//! | | boot_core_stack_start @ 0x0
+//! | | ^
+//! | Boot-core Stack | | stack
+//! | | | growth
+//! | | | direction
+//! +---------------------------------------+
+//! | | code_start @ 0x8_0000 == boot_core_stack_end_exclusive
+//! | .text |
+//! | .rodata |
+//! | .got |
+//! | |
+//! +---------------------------------------+
+//! | | data_start == code_end_exclusive
+//! | .data |
+//! | .bss |
+//! | |
+//! +---------------------------------------+
+//! | | mmio_remap_start == data_end_exclusive
+//! | VA region for MMIO remapping |
+//! | |
+//! +---------------------------------------+
+//! | | mmio_remap_end_exclusive
//! | |
pub mod mmu;
+use crate::memory::{mmu::PageAddress, Address, Physical, Virtual};
use core::cell::UnsafeCell;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -41,6 +73,15 @@
extern "Rust" {
static __code_start: UnsafeCell<()>;
static __code_end_exclusive: UnsafeCell<()>;
+
+ static __data_start: UnsafeCell<()>;
+ static __data_end_exclusive: UnsafeCell<()>;
+
+ static __mmio_remap_start: UnsafeCell<()>;
+ static __mmio_remap_end_exclusive: UnsafeCell<()>;
+
+ static __boot_core_stack_start: UnsafeCell<()>;
+ static __boot_core_stack_end_exclusive: UnsafeCell<()>;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -50,34 +91,23 @@
/// The board's physical memory map.
#[rustfmt::skip]
pub(super) mod map {
- /// The inclusive end address of the memory map.
- ///
- /// End address + 1 must be power of two.
- ///
- /// # Note
- ///
- /// RPi3 and RPi4 boards can have different amounts of RAM. To make our code lean for
- /// educational purposes, we set the max size of the address space to 4 GiB regardless of board.
- /// This way, we can map the entire range that we need (end of MMIO for RPi4) in one take.
- ///
- /// However, making this trade-off has the downside of making it possible for the CPU to assert a
- /// physical address that is not backed by any DRAM (e.g. accessing an address close to 4 GiB on
- /// an RPi3 that comes with 1 GiB of RAM). This would result in a crash or other kind of error.
- pub const END_INCLUSIVE: usize = 0xFFFF_FFFF;
-
- pub const GPIO_OFFSET: usize = 0x0020_0000;
- pub const UART_OFFSET: usize = 0x0020_1000;
+ use super::*;
/// Physical devices.
#[cfg(feature = "bsp_rpi3")]
pub mod mmio {
use super::*;
- pub const START: usize = 0x3F00_0000;
- pub const PERIPHERAL_IC_START: usize = START + 0x0000_B200;
- pub const GPIO_START: usize = START + GPIO_OFFSET;
- pub const PL011_UART_START: usize = START + UART_OFFSET;
- pub const END_INCLUSIVE: usize = 0x4000_FFFF;
+ pub const PERIPHERAL_IC_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0x3F00_B200);
+ pub const PERIPHERAL_IC_SIZE: usize = 0x24;
+
+ pub const GPIO_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0x3F20_0000);
+ pub const GPIO_SIZE: usize = 0xA0;
+
+ pub const PL011_UART_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0x3F20_1000);
+ pub const PL011_UART_SIZE: usize = 0x48;
+
+ pub const END: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0x4001_0000);
}
/// Physical devices.
@@ -85,13 +115,22 @@
pub mod mmio {
use super::*;
- pub const START: usize = 0xFE00_0000;
- pub const GPIO_START: usize = START + GPIO_OFFSET;
- pub const PL011_UART_START: usize = START + UART_OFFSET;
- pub const GICD_START: usize = 0xFF84_1000;
- pub const GICC_START: usize = 0xFF84_2000;
- pub const END_INCLUSIVE: usize = 0xFF84_FFFF;
+ pub const GPIO_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0xFE20_0000);
+ pub const GPIO_SIZE: usize = 0xA0;
+
+ pub const PL011_UART_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0xFE20_1000);
+ pub const PL011_UART_SIZE: usize = 0x48;
+
+ pub const GICD_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0xFF84_1000);
+ pub const GICD_SIZE: usize = 0x824;
+
+ pub const GICC_START: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0xFF84_2000);
+ pub const GICC_SIZE: usize = 0x14;
+
+ pub const END: Address<Physical> = Address::new(0xFF85_0000);
}
+
+ pub const END: Address<Physical> = mmio::END;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -104,15 +143,76 @@
///
/// - Value is provided by the linker script and must be trusted as-is.
#[inline(always)]
-fn code_start() -> usize {
- unsafe { __code_start.get() as usize }
+fn virt_code_start() -> PageAddress<Virtual> {
+ PageAddress::from(unsafe { __code_start.get() as usize })
}
-/// Exclusive end page address of the code segment.
+/// Size of the code segment.
+///
/// # Safety
///
/// - Value is provided by the linker script and must be trusted as-is.
#[inline(always)]
-fn code_end_exclusive() -> usize {
- unsafe { __code_end_exclusive.get() as usize }
+fn code_size() -> usize {
+ unsafe { (__code_end_exclusive.get() as usize) - (__code_start.get() as usize) }
+}
+
+/// Start page address of the data segment.
+#[inline(always)]
+fn virt_data_start() -> PageAddress<Virtual> {
+ PageAddress::from(unsafe { __data_start.get() as usize })
+}
+
+/// Size of the data segment.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Value is provided by the linker script and must be trusted as-is.
+#[inline(always)]
+fn data_size() -> usize {
+ unsafe { (__data_end_exclusive.get() as usize) - (__data_start.get() as usize) }
+}
+
+/// Start page address of the MMIO remap reservation.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Value is provided by the linker script and must be trusted as-is.
+#[inline(always)]
+fn virt_mmio_remap_start() -> PageAddress<Virtual> {
+ PageAddress::from(unsafe { __mmio_remap_start.get() as usize })
+}
+
+/// Size of the MMIO remap reservation.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Value is provided by the linker script and must be trusted as-is.
+#[inline(always)]
+fn mmio_remap_size() -> usize {
+ unsafe { (__mmio_remap_end_exclusive.get() as usize) - (__mmio_remap_start.get() as usize) }
+}
+
+/// Start page address of the boot core's stack.
+#[inline(always)]
+fn virt_boot_core_stack_start() -> PageAddress<Virtual> {
+ PageAddress::from(unsafe { __boot_core_stack_start.get() as usize })
+}
+
+/// Size of the boot core's stack.
+#[inline(always)]
+fn boot_core_stack_size() -> usize {
+ unsafe {
+ (__boot_core_stack_end_exclusive.get() as usize) - (__boot_core_stack_start.get() as usize)
+ }
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Exclusive end address of the physical address space.
+#[inline(always)]
+pub fn phys_addr_space_end_exclusive_addr() -> PageAddress<Physical> {
+ PageAddress::from(map::END)
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/common.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/common.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/common.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/common.rs
@@ -4,6 +4,30 @@
//! General purpose code.
+/// Check if a value is aligned to a given size.
+#[inline(always)]
+pub const fn is_aligned(value: usize, alignment: usize) -> bool {
+ assert!(alignment.is_power_of_two());
+
+ (value & (alignment - 1)) == 0
+}
+
+/// Align down.
+#[inline(always)]
+pub const fn align_down(value: usize, alignment: usize) -> usize {
+ assert!(alignment.is_power_of_two());
+
+ value & !(alignment - 1)
+}
+
+/// Align up.
+#[inline(always)]
+pub const fn align_up(value: usize, alignment: usize) -> usize {
+ assert!(alignment.is_power_of_two());
+
+ (value + alignment - 1) & !(alignment - 1)
+}
+
/// Convert a size into human readable format.
pub const fn size_human_readable_ceil(size: usize) -> (usize, &'static str) {
const KIB: usize = 1024;
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/lib.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/lib.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/lib.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/lib.rs
@@ -114,10 +114,13 @@
#![feature(const_option)]
#![feature(core_intrinsics)]
#![feature(format_args_nl)]
+#![feature(generic_const_exprs)]
#![feature(int_roundings)]
+#![feature(is_sorted)]
#![feature(linkage)]
#![feature(nonzero_min_max)]
#![feature(panic_info_message)]
+#![feature(step_trait)]
#![feature(trait_alias)]
#![feature(unchecked_math)]
#![no_std]
@@ -184,6 +187,17 @@
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
exception::handling_init();
+
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => panic!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string),
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ panic!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
+ }
+
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
test_main();
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/main.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/main.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/main.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/main.rs
@@ -26,14 +26,19 @@
/// IRQSafeNullLocks instead of spinlocks), will fail to work (properly) on the RPi SoCs.
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
- use memory::mmu::interface::MMU;
-
exception::handling_init();
- if let Err(string) = memory::mmu::mmu().enable_mmu_and_caching() {
- panic!("MMU: {}", string);
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => panic!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string),
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ panic!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
}
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
+
// Initialize the BSP driver subsystem.
if let Err(x) = bsp::driver::init() {
panic!("Error initializing BSP driver subsystem: {}", x);
@@ -57,8 +62,8 @@
info!("{}", libkernel::version());
info!("Booting on: {}", bsp::board_name());
- info!("MMU online. Special regions:");
- bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout().print_layout();
+ info!("MMU online:");
+ memory::mmu::kernel_print_mappings();
let (_, privilege_level) = exception::current_privilege_level();
info!("Current privilege level: {}", privilege_level);
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/mapping_record.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/mapping_record.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/mapping_record.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/mapping_record.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,238 @@
+// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
+//
+// Copyright (c) 2020-2023 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
+
+//! A record of mapped pages.
+
+use super::{
+ AccessPermissions, Address, AttributeFields, MMIODescriptor, MemAttributes, MemoryRegion,
+ Physical, Virtual,
+};
+use crate::{bsp, common, info, synchronization, synchronization::InitStateLock, warn};
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Private Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Type describing a virtual memory mapping.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+struct MappingRecordEntry {
+ pub users: [Option<&'static str>; 5],
+ pub phys_start_addr: Address<Physical>,
+ pub virt_start_addr: Address<Virtual>,
+ pub num_pages: usize,
+ pub attribute_fields: AttributeFields,
+}
+
+struct MappingRecord {
+ inner: [Option<MappingRecordEntry>; 12],
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Global instances
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+static KERNEL_MAPPING_RECORD: InitStateLock<MappingRecord> =
+ InitStateLock::new(MappingRecord::new());
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Private Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl MappingRecordEntry {
+ pub fn new(
+ name: &'static str,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+ ) -> Self {
+ Self {
+ users: [Some(name), None, None, None, None],
+ phys_start_addr: phys_region.start_addr(),
+ virt_start_addr: virt_region.start_addr(),
+ num_pages: phys_region.num_pages(),
+ attribute_fields: *attr,
+ }
+ }
+
+ fn find_next_free_user(&mut self) -> Result<&mut Option<&'static str>, &'static str> {
+ if let Some(x) = self.users.iter_mut().find(|x| x.is_none()) {
+ return Ok(x);
+ };
+
+ Err("Storage for user info exhausted")
+ }
+
+ pub fn add_user(&mut self, user: &'static str) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let x = self.find_next_free_user()?;
+ *x = Some(user);
+ Ok(())
+ }
+}
+
+impl MappingRecord {
+ pub const fn new() -> Self {
+ Self { inner: [None; 12] }
+ }
+
+ fn size(&self) -> usize {
+ self.inner.iter().filter(|x| x.is_some()).count()
+ }
+
+ fn sort(&mut self) {
+ let upper_bound_exclusive = self.size();
+ let entries = &mut self.inner[0..upper_bound_exclusive];
+
+ if !entries.is_sorted_by_key(|item| item.unwrap().virt_start_addr) {
+ entries.sort_unstable_by_key(|item| item.unwrap().virt_start_addr)
+ }
+ }
+
+ fn find_next_free(&mut self) -> Result<&mut Option<MappingRecordEntry>, &'static str> {
+ if let Some(x) = self.inner.iter_mut().find(|x| x.is_none()) {
+ return Ok(x);
+ }
+
+ Err("Storage for mapping info exhausted")
+ }
+
+ fn find_duplicate(
+ &mut self,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ ) -> Option<&mut MappingRecordEntry> {
+ self.inner
+ .iter_mut()
+ .filter_map(|x| x.as_mut())
+ .filter(|x| x.attribute_fields.mem_attributes == MemAttributes::Device)
+ .find(|x| {
+ if x.phys_start_addr != phys_region.start_addr() {
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ if x.num_pages != phys_region.num_pages() {
+ return false;
+ }
+
+ true
+ })
+ }
+
+ pub fn add(
+ &mut self,
+ name: &'static str,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+ ) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ let x = self.find_next_free()?;
+
+ *x = Some(MappingRecordEntry::new(
+ name,
+ virt_region,
+ phys_region,
+ attr,
+ ));
+
+ self.sort();
+
+ Ok(())
+ }
+
+ pub fn print(&self) {
+ info!(" -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
+ info!(
+ " {:^44} {:^30} {:^7} {:^9} {:^35}",
+ "Virtual", "Physical", "Size", "Attr", "Entity"
+ );
+ info!(" -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
+
+ for i in self.inner.iter().flatten() {
+ let size = i.num_pages * bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE;
+ let virt_start = i.virt_start_addr;
+ let virt_end_inclusive = virt_start + (size - 1);
+ let phys_start = i.phys_start_addr;
+ let phys_end_inclusive = phys_start + (size - 1);
+
+ let (size, unit) = common::size_human_readable_ceil(size);
+
+ let attr = match i.attribute_fields.mem_attributes {
+ MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM => "C",
+ MemAttributes::Device => "Dev",
+ };
+
+ let acc_p = match i.attribute_fields.acc_perms {
+ AccessPermissions::ReadOnly => "RO",
+ AccessPermissions::ReadWrite => "RW",
+ };
+
+ let xn = if i.attribute_fields.execute_never {
+ "XN"
+ } else {
+ "X"
+ };
+
+ info!(
+ " {}..{} --> {}..{} | {:>3} {} | {:<3} {} {:<2} | {}",
+ virt_start,
+ virt_end_inclusive,
+ phys_start,
+ phys_end_inclusive,
+ size,
+ unit,
+ attr,
+ acc_p,
+ xn,
+ i.users[0].unwrap()
+ );
+
+ for k in i.users[1..].iter() {
+ if let Some(additional_user) = *k {
+ info!(
+ " | {}",
+ additional_user
+ );
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ info!(" -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
+ }
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+use synchronization::interface::ReadWriteEx;
+
+/// Add an entry to the mapping info record.
+pub fn kernel_add(
+ name: &'static str,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ KERNEL_MAPPING_RECORD.write(|mr| mr.add(name, virt_region, phys_region, attr))
+}
+
+pub fn kernel_find_and_insert_mmio_duplicate(
+ mmio_descriptor: &MMIODescriptor,
+ new_user: &'static str,
+) -> Option<Address<Virtual>> {
+ let phys_region: MemoryRegion<Physical> = (*mmio_descriptor).into();
+
+ KERNEL_MAPPING_RECORD.write(|mr| {
+ let dup = mr.find_duplicate(&phys_region)?;
+
+ if let Err(x) = dup.add_user(new_user) {
+ warn!("{}", x);
+ }
+
+ Some(dup.virt_start_addr)
+ })
+}
+
+/// Human-readable print of all recorded kernel mappings.
+pub fn kernel_print() {
+ KERNEL_MAPPING_RECORD.read(|mr| mr.print());
+}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/page_alloc.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/page_alloc.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/page_alloc.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/page_alloc.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
+//
+// Copyright (c) 2021-2023 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
+
+//! Page allocation.
+
+use super::MemoryRegion;
+use crate::{
+ memory::{AddressType, Virtual},
+ synchronization::IRQSafeNullLock,
+ warn,
+};
+use core::num::NonZeroUsize;
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// A page allocator that can be lazyily initialized.
+pub struct PageAllocator<ATYPE: AddressType> {
+ pool: Option<MemoryRegion<ATYPE>>,
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Global instances
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+static KERNEL_MMIO_VA_ALLOCATOR: IRQSafeNullLock<PageAllocator<Virtual>> =
+ IRQSafeNullLock::new(PageAllocator::new());
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Return a reference to the kernel's MMIO virtual address allocator.
+pub fn kernel_mmio_va_allocator() -> &'static IRQSafeNullLock<PageAllocator<Virtual>> {
+ &KERNEL_MMIO_VA_ALLOCATOR
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> PageAllocator<ATYPE> {
+ /// Create an instance.
+ pub const fn new() -> Self {
+ Self { pool: None }
+ }
+
+ /// Initialize the allocator.
+ pub fn init(&mut self, pool: MemoryRegion<ATYPE>) {
+ if self.pool.is_some() {
+ warn!("Already initialized");
+ return;
+ }
+
+ self.pool = Some(pool);
+ }
+
+ /// Allocate a number of pages.
+ pub fn alloc(
+ &mut self,
+ num_requested_pages: NonZeroUsize,
+ ) -> Result<MemoryRegion<ATYPE>, &'static str> {
+ if self.pool.is_none() {
+ return Err("Allocator not initialized");
+ }
+
+ self.pool
+ .as_mut()
+ .unwrap()
+ .take_first_n_pages(num_requested_pages)
+ }
+}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs
@@ -8,7 +8,91 @@
#[path = "../../_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu/translation_table.rs"]
mod arch_translation_table;
+use super::{AttributeFields, MemoryRegion};
+use crate::memory::{Address, Physical, Virtual};
+
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Architectural Public Reexports
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-pub use arch_translation_table::KernelTranslationTable;
+#[cfg(target_arch = "aarch64")]
+pub use arch_translation_table::FixedSizeTranslationTable;
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Translation table interfaces.
+pub mod interface {
+ use super::*;
+
+ /// Translation table operations.
+ pub trait TranslationTable {
+ /// Anything that needs to run before any of the other provided functions can be used.
+ ///
+ /// # Safety
+ ///
+ /// - Implementor must ensure that this function can run only once or is harmless if invoked
+ /// multiple times.
+ fn init(&mut self);
+
+ /// The translation table's base address to be used for programming the MMU.
+ fn phys_base_address(&self) -> Address<Physical>;
+
+ /// Map the given virtual memory region to the given physical memory region.
+ ///
+ /// # Safety
+ ///
+ /// - Using wrong attributes can cause multiple issues of different nature in the system.
+ /// - It is not required that the architectural implementation prevents aliasing. That is,
+ /// mapping to the same physical memory using multiple virtual addresses, which would
+ /// break Rust's ownership assumptions. This should be protected against in the kernel's
+ /// generic MMU code.
+ unsafe fn map_at(
+ &mut self,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+ ) -> Result<(), &'static str>;
+ }
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Testing
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+#[cfg(test)]
+mod tests {
+ use super::*;
+ use crate::memory::mmu::{AccessPermissions, MemAttributes, PageAddress};
+ use arch_translation_table::MinSizeTranslationTable;
+ use interface::TranslationTable;
+ use test_macros::kernel_test;
+
+ /// Sanity checks for the TranslationTable implementation.
+ #[kernel_test]
+ fn translationtable_implementation_sanity() {
+ // This will occupy a lot of space on the stack.
+ let mut tables = MinSizeTranslationTable::new();
+
+ tables.init();
+
+ let virt_start_page_addr: PageAddress<Virtual> = PageAddress::from(0);
+ let virt_end_exclusive_page_addr: PageAddress<Virtual> =
+ virt_start_page_addr.checked_offset(5).unwrap();
+
+ let phys_start_page_addr: PageAddress<Physical> = PageAddress::from(0);
+ let phys_end_exclusive_page_addr: PageAddress<Physical> =
+ phys_start_page_addr.checked_offset(5).unwrap();
+
+ let virt_region = MemoryRegion::new(virt_start_page_addr, virt_end_exclusive_page_addr);
+ let phys_region = MemoryRegion::new(phys_start_page_addr, phys_end_exclusive_page_addr);
+
+ let attr = AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ };
+
+ unsafe { assert_eq!(tables.map_at(&virt_region, &phys_region, &attr), Ok(())) };
+ }
+}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/types.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/types.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu/types.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu/types.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,373 @@
+// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
+//
+// Copyright (c) 2020-2023 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
+
+//! Memory Management Unit types.
+
+use crate::{
+ bsp, common,
+ memory::{Address, AddressType, Physical},
+};
+use core::{convert::From, iter::Step, num::NonZeroUsize, ops::Range};
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// A wrapper type around [Address] that ensures page alignment.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, Eq, PartialOrd, PartialEq)]
+pub struct PageAddress<ATYPE: AddressType> {
+ inner: Address<ATYPE>,
+}
+
+/// A type that describes a region of memory in quantities of pages.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, Eq, PartialOrd, PartialEq)]
+pub struct MemoryRegion<ATYPE: AddressType> {
+ start: PageAddress<ATYPE>,
+ end_exclusive: PageAddress<ATYPE>,
+}
+
+/// Architecture agnostic memory attributes.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, Eq, PartialOrd, PartialEq)]
+pub enum MemAttributes {
+ CacheableDRAM,
+ Device,
+}
+
+/// Architecture agnostic access permissions.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, Eq, PartialOrd, PartialEq)]
+pub enum AccessPermissions {
+ ReadOnly,
+ ReadWrite,
+}
+
+/// Collection of memory attributes.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, Eq, PartialOrd, PartialEq)]
+pub struct AttributeFields {
+ pub mem_attributes: MemAttributes,
+ pub acc_perms: AccessPermissions,
+ pub execute_never: bool,
+}
+
+/// An MMIO descriptor for use in device drivers.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+pub struct MMIODescriptor {
+ start_addr: Address<Physical>,
+ end_addr_exclusive: Address<Physical>,
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// PageAddress
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ /// Unwraps the value.
+ pub fn into_inner(self) -> Address<ATYPE> {
+ self.inner
+ }
+
+ /// Calculates the offset from the page address.
+ ///
+ /// `count` is in units of [PageAddress]. For example, a count of 2 means `result = self + 2 *
+ /// page_size`.
+ pub fn checked_offset(self, count: isize) -> Option<Self> {
+ if count == 0 {
+ return Some(self);
+ }
+
+ let delta = count
+ .unsigned_abs()
+ .checked_mul(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE)?;
+ let result = if count.is_positive() {
+ self.inner.as_usize().checked_add(delta)?
+ } else {
+ self.inner.as_usize().checked_sub(delta)?
+ };
+
+ Some(Self {
+ inner: Address::new(result),
+ })
+ }
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> From<usize> for PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ fn from(addr: usize) -> Self {
+ assert!(
+ common::is_aligned(addr, bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE),
+ "Input usize not page aligned"
+ );
+
+ Self {
+ inner: Address::new(addr),
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> From<Address<ATYPE>> for PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ fn from(addr: Address<ATYPE>) -> Self {
+ assert!(addr.is_page_aligned(), "Input Address not page aligned");
+
+ Self { inner: addr }
+ }
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> Step for PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ fn steps_between(start: &Self, end: &Self) -> Option<usize> {
+ if start > end {
+ return None;
+ }
+
+ // Since start <= end, do unchecked arithmetic.
+ Some(
+ (end.inner.as_usize() - start.inner.as_usize())
+ >> bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SHIFT,
+ )
+ }
+
+ fn forward_checked(start: Self, count: usize) -> Option<Self> {
+ start.checked_offset(count as isize)
+ }
+
+ fn backward_checked(start: Self, count: usize) -> Option<Self> {
+ start.checked_offset(-(count as isize))
+ }
+}
+
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// MemoryRegion
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> MemoryRegion<ATYPE> {
+ /// Create an instance.
+ pub fn new(start: PageAddress<ATYPE>, end_exclusive: PageAddress<ATYPE>) -> Self {
+ assert!(start <= end_exclusive);
+
+ Self {
+ start,
+ end_exclusive,
+ }
+ }
+
+ fn as_range(&self) -> Range<PageAddress<ATYPE>> {
+ self.into_iter()
+ }
+
+ /// Returns the start page address.
+ pub fn start_page_addr(&self) -> PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ self.start
+ }
+
+ /// Returns the start address.
+ pub fn start_addr(&self) -> Address<ATYPE> {
+ self.start.into_inner()
+ }
+
+ /// Returns the exclusive end page address.
+ pub fn end_exclusive_page_addr(&self) -> PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ self.end_exclusive
+ }
+
+ /// Returns the exclusive end page address.
+ pub fn end_inclusive_page_addr(&self) -> PageAddress<ATYPE> {
+ self.end_exclusive.checked_offset(-1).unwrap()
+ }
+
+ /// Checks if self contains an address.
+ pub fn contains(&self, addr: Address<ATYPE>) -> bool {
+ let page_addr = PageAddress::from(addr.align_down_page());
+ self.as_range().contains(&page_addr)
+ }
+
+ /// Checks if there is an overlap with another memory region.
+ pub fn overlaps(&self, other_region: &Self) -> bool {
+ let self_range = self.as_range();
+
+ self_range.contains(&other_region.start_page_addr())
+ || self_range.contains(&other_region.end_inclusive_page_addr())
+ }
+
+ /// Returns the number of pages contained in this region.
+ pub fn num_pages(&self) -> usize {
+ PageAddress::steps_between(&self.start, &self.end_exclusive).unwrap()
+ }
+
+ /// Returns the size in bytes of this region.
+ pub fn size(&self) -> usize {
+ // Invariant: start <= end_exclusive, so do unchecked arithmetic.
+ let end_exclusive = self.end_exclusive.into_inner().as_usize();
+ let start = self.start.into_inner().as_usize();
+
+ end_exclusive - start
+ }
+
+ /// Splits the MemoryRegion like:
+ ///
+ /// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ /// | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
+ /// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ /// ^ ^ ^
+ /// | | |
+ /// left_start left_end_exclusive |
+ /// |
+ /// ^ |
+ /// | |
+ /// right_start right_end_exclusive
+ ///
+ /// Left region is returned to the caller. Right region is the new region for this struct.
+ pub fn take_first_n_pages(&mut self, num_pages: NonZeroUsize) -> Result<Self, &'static str> {
+ let count: usize = num_pages.into();
+
+ let left_end_exclusive = self.start.checked_offset(count as isize);
+ let left_end_exclusive = match left_end_exclusive {
+ None => return Err("Overflow while calculating left_end_exclusive"),
+ Some(x) => x,
+ };
+
+ if left_end_exclusive > self.end_exclusive {
+ return Err("Not enough free pages");
+ }
+
+ let allocation = Self {
+ start: self.start,
+ end_exclusive: left_end_exclusive,
+ };
+ self.start = left_end_exclusive;
+
+ Ok(allocation)
+ }
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> IntoIterator for MemoryRegion<ATYPE> {
+ type Item = PageAddress<ATYPE>;
+ type IntoIter = Range<Self::Item>;
+
+ fn into_iter(self) -> Self::IntoIter {
+ Range {
+ start: self.start,
+ end: self.end_exclusive,
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+impl From<MMIODescriptor> for MemoryRegion<Physical> {
+ fn from(desc: MMIODescriptor) -> Self {
+ let start = PageAddress::from(desc.start_addr.align_down_page());
+ let end_exclusive = PageAddress::from(desc.end_addr_exclusive().align_up_page());
+
+ Self {
+ start,
+ end_exclusive,
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// MMIODescriptor
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl MMIODescriptor {
+ /// Create an instance.
+ pub const fn new(start_addr: Address<Physical>, size: usize) -> Self {
+ assert!(size > 0);
+ let end_addr_exclusive = Address::new(start_addr.as_usize() + size);
+
+ Self {
+ start_addr,
+ end_addr_exclusive,
+ }
+ }
+
+ /// Return the start address.
+ pub const fn start_addr(&self) -> Address<Physical> {
+ self.start_addr
+ }
+
+ /// Return the exclusive end address.
+ pub fn end_addr_exclusive(&self) -> Address<Physical> {
+ self.end_addr_exclusive
+ }
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Testing
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+#[cfg(test)]
+mod tests {
+ use super::*;
+ use crate::memory::Virtual;
+ use test_macros::kernel_test;
+
+ /// Sanity of [PageAddress] methods.
+ #[kernel_test]
+ fn pageaddress_type_method_sanity() {
+ let page_addr: PageAddress<Virtual> =
+ PageAddress::from(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE * 2);
+
+ assert_eq!(
+ page_addr.checked_offset(-2),
+ Some(PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(0))
+ );
+
+ assert_eq!(
+ page_addr.checked_offset(2),
+ Some(PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(
+ bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE * 4
+ ))
+ );
+
+ assert_eq!(
+ PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(0).checked_offset(0),
+ Some(PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(0))
+ );
+ assert_eq!(PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(0).checked_offset(-1), None);
+
+ let max_page_addr = Address::<Virtual>::new(usize::MAX).align_down_page();
+ assert_eq!(
+ PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(max_page_addr).checked_offset(1),
+ None
+ );
+
+ let zero = PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(0);
+ let three = PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE * 3);
+ assert_eq!(PageAddress::steps_between(&zero, &three), Some(3));
+ }
+
+ /// Sanity of [MemoryRegion] methods.
+ #[kernel_test]
+ fn memoryregion_type_method_sanity() {
+ let zero = PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(0);
+ let zero_region = MemoryRegion::new(zero, zero);
+ assert_eq!(zero_region.num_pages(), 0);
+ assert_eq!(zero_region.size(), 0);
+
+ let one = PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE);
+ let one_region = MemoryRegion::new(zero, one);
+ assert_eq!(one_region.num_pages(), 1);
+ assert_eq!(one_region.size(), bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE);
+
+ let three = PageAddress::<Virtual>::from(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE * 3);
+ let mut three_region = MemoryRegion::new(zero, three);
+ assert!(three_region.contains(zero.into_inner()));
+ assert!(!three_region.contains(three.into_inner()));
+ assert!(three_region.overlaps(&one_region));
+
+ let allocation = three_region
+ .take_first_n_pages(NonZeroUsize::new(2).unwrap())
+ .unwrap();
+ assert_eq!(allocation.num_pages(), 2);
+ assert_eq!(three_region.num_pages(), 1);
+
+ for (i, alloc) in allocation.into_iter().enumerate() {
+ assert_eq!(
+ alloc.into_inner().as_usize(),
+ i * bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE
+ );
+ }
+ }
+}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory/mmu.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory/mmu.rs
@@ -3,30 +3,24 @@
// Copyright (c) 2020-2023 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
//! Memory Management Unit.
-//!
-//! In order to decouple `BSP` and `arch` parts of the MMU code (to keep them pluggable), this file
-//! provides types for composing an architecture-agnostic description of the kernel's virtual memory
-//! layout.
-//!
-//! The `BSP` provides such a description through the `bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout()`
-//! function.
-//!
-//! The `MMU` driver of the `arch` code uses `bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout()` to compile and
-//! install respective translation tables.
#[cfg(target_arch = "aarch64")]
#[path = "../_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs"]
mod arch_mmu;
+mod mapping_record;
+mod page_alloc;
mod translation_table;
+mod types;
-use crate::common;
-use core::{fmt, ops::RangeInclusive};
+use crate::{
+ bsp,
+ memory::{Address, Physical, Virtual},
+ synchronization, warn,
+};
+use core::{fmt, num::NonZeroUsize};
-//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-// Architectural Public Reexports
-//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-pub use arch_mmu::mmu;
+pub use types::*;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Public Definitions
@@ -46,13 +40,15 @@
/// MMU functions.
pub trait MMU {
- /// Called by the kernel during early init. Supposed to take the translation tables from the
- /// `BSP`-supplied `virt_mem_layout()` and install/activate them for the respective MMU.
+ /// Turns on the MMU for the first time and enables data and instruction caching.
///
/// # Safety
///
/// - Changes the HW's global state.
- unsafe fn enable_mmu_and_caching(&self) -> Result<(), MMUEnableError>;
+ unsafe fn enable_mmu_and_caching(
+ &self,
+ phys_tables_base_addr: Address<Physical>,
+ ) -> Result<(), MMUEnableError>;
/// Returns true if the MMU is enabled, false otherwise.
fn is_enabled(&self) -> bool;
@@ -65,55 +61,51 @@
/// Describes properties of an address space.
pub struct AddressSpace<const AS_SIZE: usize>;
-/// Architecture agnostic translation types.
-#[allow(missing_docs)]
-#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
-pub enum Translation {
- Identity,
- Offset(usize),
-}
-
-/// Architecture agnostic memory attributes.
-#[allow(missing_docs)]
-#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
-pub enum MemAttributes {
- CacheableDRAM,
- Device,
-}
-
-/// Architecture agnostic access permissions.
-#[allow(missing_docs)]
-#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
-pub enum AccessPermissions {
- ReadOnly,
- ReadWrite,
-}
-
-/// Collection of memory attributes.
-#[allow(missing_docs)]
-#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
-pub struct AttributeFields {
- pub mem_attributes: MemAttributes,
- pub acc_perms: AccessPermissions,
- pub execute_never: bool,
+/// Intended to be implemented for [`AddressSpace`].
+pub trait AssociatedTranslationTable {
+ /// A translation table whose address range is:
+ ///
+ /// [AS_SIZE - 1, 0]
+ type TableStartFromBottom;
}
-/// Architecture agnostic descriptor for a memory range.
-#[allow(missing_docs)]
-pub struct TranslationDescriptor {
- pub name: &'static str,
- pub virtual_range: fn() -> RangeInclusive<usize>,
- pub physical_range_translation: Translation,
- pub attribute_fields: AttributeFields,
-}
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Private Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+use interface::MMU;
+use synchronization::interface::*;
+use translation_table::interface::TranslationTable;
+
+/// Query the BSP for the reserved virtual addresses for MMIO remapping and initialize the kernel's
+/// MMIO VA allocator with it.
+fn kernel_init_mmio_va_allocator() {
+ let region = bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mmio_remap_region();
+
+ page_alloc::kernel_mmio_va_allocator().lock(|allocator| allocator.init(region));
+}
+
+/// Map a region in the kernel's translation tables.
+///
+/// No input checks done, input is passed through to the architectural implementation.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - See `map_at()`.
+/// - Does not prevent aliasing.
+unsafe fn kernel_map_at_unchecked(
+ name: &'static str,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ bsp::memory::mmu::kernel_translation_tables()
+ .write(|tables| tables.map_at(virt_region, phys_region, attr))?;
-/// Type for expressing the kernel's virtual memory layout.
-pub struct KernelVirtualLayout<const NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES: usize> {
- /// The last (inclusive) address of the address space.
- max_virt_addr_inclusive: usize,
+ if let Err(x) = mapping_record::kernel_add(name, virt_region, phys_region, attr) {
+ warn!("{}", x);
+ }
- /// Array of descriptors for non-standard (normal cacheable DRAM) memory regions.
- inner: [TranslationDescriptor; NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES],
+ Ok(())
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -133,6 +125,9 @@
/// The granule's size.
pub const SIZE: usize = Self::size_checked();
+ /// The granule's mask.
+ pub const MASK: usize = Self::SIZE - 1;
+
/// The granule's shift, aka log2(size).
pub const SHIFT: usize = Self::SIZE.trailing_zeros() as usize;
@@ -160,98 +155,147 @@
}
}
-impl Default for AttributeFields {
- fn default() -> AttributeFields {
- AttributeFields {
- mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
- acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
- execute_never: true,
- }
+/// Raw mapping of a virtual to physical region in the kernel translation tables.
+///
+/// Prevents mapping into the MMIO range of the tables.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - See `kernel_map_at_unchecked()`.
+/// - Does not prevent aliasing. Currently, the callers must be trusted.
+pub unsafe fn kernel_map_at(
+ name: &'static str,
+ virt_region: &MemoryRegion<Virtual>,
+ phys_region: &MemoryRegion<Physical>,
+ attr: &AttributeFields,
+) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ if bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mmio_remap_region().overlaps(virt_region) {
+ return Err("Attempt to manually map into MMIO region");
}
-}
-/// Human-readable output of a TranslationDescriptor.
-impl fmt::Display for TranslationDescriptor {
- fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
- // Call the function to which self.range points, and dereference the result, which causes
- // Rust to copy the value.
- let start = *(self.virtual_range)().start();
- let end = *(self.virtual_range)().end();
- let size = end - start + 1;
-
- let (size, unit) = common::size_human_readable_ceil(size);
-
- let attr = match self.attribute_fields.mem_attributes {
- MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM => "C",
- MemAttributes::Device => "Dev",
- };
-
- let acc_p = match self.attribute_fields.acc_perms {
- AccessPermissions::ReadOnly => "RO",
- AccessPermissions::ReadWrite => "RW",
- };
+ kernel_map_at_unchecked(name, virt_region, phys_region, attr)?;
- let xn = if self.attribute_fields.execute_never {
- "PXN"
- } else {
- "PX"
- };
-
- write!(
- f,
- " {:#010x} - {:#010x} | {: >3} {} | {: <3} {} {: <3} | {}",
- start, end, size, unit, attr, acc_p, xn, self.name
- )
- }
+ Ok(())
}
-impl<const NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES: usize> KernelVirtualLayout<{ NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES }> {
- /// Create a new instance.
- pub const fn new(max: usize, layout: [TranslationDescriptor; NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES]) -> Self {
- Self {
- max_virt_addr_inclusive: max,
- inner: layout,
- }
- }
+/// MMIO remapping in the kernel translation tables.
+///
+/// Typically used by device drivers.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Same as `kernel_map_at_unchecked()`, minus the aliasing part.
+pub unsafe fn kernel_map_mmio(
+ name: &'static str,
+ mmio_descriptor: &MMIODescriptor,
+) -> Result<Address<Virtual>, &'static str> {
+ let phys_region = MemoryRegion::from(*mmio_descriptor);
+ let offset_into_start_page = mmio_descriptor.start_addr().offset_into_page();
+
+ // Check if an identical region has been mapped for another driver. If so, reuse it.
+ let virt_addr = if let Some(addr) =
+ mapping_record::kernel_find_and_insert_mmio_duplicate(mmio_descriptor, name)
+ {
+ addr
+ // Otherwise, allocate a new region and map it.
+ } else {
+ let num_pages = match NonZeroUsize::new(phys_region.num_pages()) {
+ None => return Err("Requested 0 pages"),
+ Some(x) => x,
+ };
- /// For a virtual address, find and return the physical output address and corresponding
- /// attributes.
- ///
- /// If the address is not found in `inner`, return an identity mapped default with normal
- /// cacheable DRAM attributes.
- pub fn virt_addr_properties(
- &self,
- virt_addr: usize,
- ) -> Result<(usize, AttributeFields), &'static str> {
- if virt_addr > self.max_virt_addr_inclusive {
- return Err("Address out of range");
- }
+ let virt_region =
+ page_alloc::kernel_mmio_va_allocator().lock(|allocator| allocator.alloc(num_pages))?;
- for i in self.inner.iter() {
- if (i.virtual_range)().contains(&virt_addr) {
- let output_addr = match i.physical_range_translation {
- Translation::Identity => virt_addr,
- Translation::Offset(a) => a + (virt_addr - (i.virtual_range)().start()),
- };
+ kernel_map_at_unchecked(
+ name,
+ &virt_region,
+ &phys_region,
+ &AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::Device,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ },
+ )?;
+
+ virt_region.start_addr()
+ };
+
+ Ok(virt_addr + offset_into_start_page)
+}
+
+/// Map the kernel's binary. Returns the translation table's base address.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - See [`bsp::memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary()`].
+pub unsafe fn kernel_map_binary() -> Result<Address<Physical>, &'static str> {
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr =
+ bsp::memory::mmu::kernel_translation_tables().write(|tables| {
+ tables.init();
+ tables.phys_base_address()
+ });
+
+ bsp::memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary()?;
+
+ Ok(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr)
+}
+
+/// Enable the MMU and data + instruction caching.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Crucial function during kernel init. Changes the the complete memory view of the processor.
+pub unsafe fn enable_mmu_and_caching(
+ phys_tables_base_addr: Address<Physical>,
+) -> Result<(), MMUEnableError> {
+ arch_mmu::mmu().enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_tables_base_addr)
+}
+
+/// Finish initialization of the MMU subsystem.
+pub fn post_enable_init() {
+ kernel_init_mmio_va_allocator();
+}
+
+/// Human-readable print of all recorded kernel mappings.
+pub fn kernel_print_mappings() {
+ mapping_record::kernel_print()
+}
- return Ok((output_addr, i.attribute_fields));
- }
- }
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Testing
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Ok((virt_addr, AttributeFields::default()))
- }
+#[cfg(test)]
+mod tests {
+ use super::*;
+ use crate::memory::mmu::{AccessPermissions, MemAttributes, PageAddress};
+ use test_macros::kernel_test;
- /// Print the memory layout.
- pub fn print_layout(&self) {
- use crate::info;
+ /// Check that you cannot map into the MMIO VA range from kernel_map_at().
+ #[kernel_test]
+ fn no_manual_mmio_map() {
+ let phys_start_page_addr: PageAddress<Physical> = PageAddress::from(0);
+ let phys_end_exclusive_page_addr: PageAddress<Physical> =
+ phys_start_page_addr.checked_offset(5).unwrap();
+ let phys_region = MemoryRegion::new(phys_start_page_addr, phys_end_exclusive_page_addr);
+
+ let num_pages = NonZeroUsize::new(phys_region.num_pages()).unwrap();
+ let virt_region = page_alloc::kernel_mmio_va_allocator()
+ .lock(|allocator| allocator.alloc(num_pages))
+ .unwrap();
- for i in self.inner.iter() {
- info!("{}", i);
- }
- }
+ let attr = AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ };
- #[cfg(test)]
- pub fn inner(&self) -> &[TranslationDescriptor; NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES] {
- &self.inner
+ unsafe {
+ assert_eq!(
+ kernel_map_at("test", &virt_region, &phys_region, &attr),
+ Err("Attempt to manually map into MMIO region")
+ )
+ };
}
}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/src/memory.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/src/memory.rs
@@ -5,3 +5,163 @@
//! Memory Management.
pub mod mmu;
+
+use crate::{bsp, common};
+use core::{
+ fmt,
+ marker::PhantomData,
+ ops::{Add, Sub},
+};
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Metadata trait for marking the type of an address.
+pub trait AddressType: Copy + Clone + PartialOrd + PartialEq + Ord + Eq {}
+
+/// Zero-sized type to mark a physical address.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialOrd, PartialEq, Ord, Eq)]
+pub enum Physical {}
+
+/// Zero-sized type to mark a virtual address.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialOrd, PartialEq, Ord, Eq)]
+pub enum Virtual {}
+
+/// Generic address type.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialOrd, PartialEq, Ord, Eq)]
+pub struct Address<ATYPE: AddressType> {
+ value: usize,
+ _address_type: PhantomData<fn() -> ATYPE>,
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl AddressType for Physical {}
+impl AddressType for Virtual {}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> Address<ATYPE> {
+ /// Create an instance.
+ pub const fn new(value: usize) -> Self {
+ Self {
+ value,
+ _address_type: PhantomData,
+ }
+ }
+
+ /// Convert to usize.
+ pub const fn as_usize(self) -> usize {
+ self.value
+ }
+
+ /// Align down to page size.
+ #[must_use]
+ pub const fn align_down_page(self) -> Self {
+ let aligned = common::align_down(self.value, bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE);
+
+ Self::new(aligned)
+ }
+
+ /// Align up to page size.
+ #[must_use]
+ pub const fn align_up_page(self) -> Self {
+ let aligned = common::align_up(self.value, bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE);
+
+ Self::new(aligned)
+ }
+
+ /// Checks if the address is page aligned.
+ pub const fn is_page_aligned(&self) -> bool {
+ common::is_aligned(self.value, bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE)
+ }
+
+ /// Return the address' offset into the corresponding page.
+ pub const fn offset_into_page(&self) -> usize {
+ self.value & bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::MASK
+ }
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> Add<usize> for Address<ATYPE> {
+ type Output = Self;
+
+ #[inline(always)]
+ fn add(self, rhs: usize) -> Self::Output {
+ match self.value.checked_add(rhs) {
+ None => panic!("Overflow on Address::add"),
+ Some(x) => Self::new(x),
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+impl<ATYPE: AddressType> Sub<Address<ATYPE>> for Address<ATYPE> {
+ type Output = Self;
+
+ #[inline(always)]
+ fn sub(self, rhs: Address<ATYPE>) -> Self::Output {
+ match self.value.checked_sub(rhs.value) {
+ None => panic!("Overflow on Address::sub"),
+ Some(x) => Self::new(x),
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+impl fmt::Display for Address<Physical> {
+ // Don't expect to see physical addresses greater than 40 bit.
+ fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
+ let q3: u8 = ((self.value >> 32) & 0xff) as u8;
+ let q2: u16 = ((self.value >> 16) & 0xffff) as u16;
+ let q1: u16 = (self.value & 0xffff) as u16;
+
+ write!(f, "0x")?;
+ write!(f, "{:02x}_", q3)?;
+ write!(f, "{:04x}_", q2)?;
+ write!(f, "{:04x}", q1)
+ }
+}
+
+impl fmt::Display for Address<Virtual> {
+ fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
+ let q4: u16 = ((self.value >> 48) & 0xffff) as u16;
+ let q3: u16 = ((self.value >> 32) & 0xffff) as u16;
+ let q2: u16 = ((self.value >> 16) & 0xffff) as u16;
+ let q1: u16 = (self.value & 0xffff) as u16;
+
+ write!(f, "0x")?;
+ write!(f, "{:04x}_", q4)?;
+ write!(f, "{:04x}_", q3)?;
+ write!(f, "{:04x}_", q2)?;
+ write!(f, "{:04x}", q1)
+ }
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Testing
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+#[cfg(test)]
+mod tests {
+ use super::*;
+ use test_macros::kernel_test;
+
+ /// Sanity of [Address] methods.
+ #[kernel_test]
+ fn address_type_method_sanity() {
+ let addr = Address::<Virtual>::new(bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE + 100);
+
+ assert_eq!(
+ addr.align_down_page().as_usize(),
+ bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE
+ );
+
+ assert_eq!(
+ addr.align_up_page().as_usize(),
+ bsp::memory::mmu::KernelGranule::SIZE * 2
+ );
+
+ assert!(!addr.is_page_aligned());
+
+ assert_eq!(addr.offset_into_page(), 100);
+ }
+}
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/00_console_sanity.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/00_console_sanity.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/00_console_sanity.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/00_console_sanity.rs
@@ -11,13 +11,24 @@
/// Console tests should time out on the I/O harness in case of panic.
mod panic_wait_forever;
-use libkernel::{bsp, console, cpu, exception, print};
+use libkernel::{bsp, console, cpu, exception, memory, print};
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
use console::console;
exception::handling_init();
+
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => panic!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string),
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ panic!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
+ }
+
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
// Handshake
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/01_timer_sanity.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/01_timer_sanity.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/01_timer_sanity.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/01_timer_sanity.rs
@@ -11,12 +11,23 @@
#![test_runner(libkernel::test_runner)]
use core::time::Duration;
-use libkernel::{bsp, cpu, exception, time};
+use libkernel::{bsp, cpu, exception, memory, time};
use test_macros::kernel_test;
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
exception::handling_init();
+
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => panic!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string),
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ panic!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
+ }
+
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
// Depending on CPU arch, some timer bring-up code could go here. Not needed for the RPi.
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/02_exception_sync_page_fault.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/02_exception_sync_page_fault.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/02_exception_sync_page_fault.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/02_exception_sync_page_fault.rs
@@ -21,19 +21,27 @@
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
- use memory::mmu::interface::MMU;
-
exception::handling_init();
- bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
// This line will be printed as the test header.
println!("Testing synchronous exception handling by causing a page fault");
- if let Err(string) = memory::mmu::mmu().enable_mmu_and_caching() {
- info!("MMU: {}", string);
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => {
+ info!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string);
+ cpu::qemu_exit_failure()
+ }
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ info!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
cpu::qemu_exit_failure()
}
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
+ bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
+
info!("Writing beyond mapped area to address 9 GiB...");
let big_addr: u64 = 9 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
core::ptr::read_volatile(big_addr as *mut u64);
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/03_exception_restore_sanity.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/03_exception_restore_sanity.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/03_exception_restore_sanity.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/03_exception_restore_sanity.rs
@@ -30,19 +30,27 @@
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
- use memory::mmu::interface::MMU;
-
exception::handling_init();
- bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
// This line will be printed as the test header.
println!("Testing exception restore");
- if let Err(string) = memory::mmu::mmu().enable_mmu_and_caching() {
- info!("MMU: {}", string);
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => {
+ info!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string);
+ cpu::qemu_exit_failure()
+ }
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ info!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
cpu::qemu_exit_failure()
}
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
+ bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
+
info!("Making a dummy system call");
// Calling this inside a function indirectly tests if the link register is restored properly.
diff -uNr 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/04_exception_irq_sanity.rs 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/04_exception_irq_sanity.rs
--- 13_exceptions_part2_peripheral_IRQs/kernel/tests/04_exception_irq_sanity.rs
+++ 14_virtual_mem_part2_mmio_remap/kernel/tests/04_exception_irq_sanity.rs
@@ -10,14 +10,25 @@
#![reexport_test_harness_main = "test_main"]
#![test_runner(libkernel::test_runner)]
-use libkernel::{bsp, cpu, exception};
+use libkernel::{bsp, cpu, exception, memory};
use test_macros::kernel_test;
#[no_mangle]
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
+ exception::handling_init();
+
+ let phys_kernel_tables_base_addr = match memory::mmu::kernel_map_binary() {
+ Err(string) => panic!("Error mapping kernel binary: {}", string),
+ Ok(addr) => addr,
+ };
+
+ if let Err(e) = memory::mmu::enable_mmu_and_caching(phys_kernel_tables_base_addr) {
+ panic!("Enabling MMU failed: {}", e);
+ }
+
+ memory::mmu::post_enable_init();
bsp::driver::qemu_bring_up_console();
- exception::handling_init();
exception::asynchronous::local_irq_unmask();
test_main();