|
|
4 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| .vscode | 4 years ago | |
| src | 4 years ago | |
| Cargo.lock | 4 years ago | |
| Cargo.toml | 4 years ago | |
| Makefile | 4 years ago | |
| README.md | 4 years ago | |
| build.rs | 4 years ago | |
README.md
Tutorial 11 - Virtual Memory
tl;dr
The MMU is turned on; A simple scheme is used: static 64 KiB translation tables; For educational
purposes, we write to a remapped UART.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- MMU and paging theory
- Approach
- Address translation examples
- Zero-cost abstraction
- Test it
- Diff to previous
Introduction
Virtual memory is an immensely complex, but important and powerful topic. In this tutorial, we start
slow and easy by switching on the MMU, using static translation tables and mapping everything at
once.
MMU and paging theory
At this point, we will not re-invent the wheel and go into detailed descriptions of how paging in modern application-grade processors works. The internet is full of great resources regarding this topic, and we encourage you to read some of it to get a high-level understanding of the topic.
To follow the rest of this AArch64 specific tutorial, I strongly recommend that you stop right
here and first read Chapter 12 of the ARM Cortex-A Series Programmer's Guide for ARMv8-A before
you continue. This will set you up with all the AArch64-specific knowledge needed to follow along.
Back from reading Chapter 12 already? Good job 👍!
Approach
- The generic
kernelpart:src/memory/mmu.rsprovides architecture-agnostic descriptor types for composing a high-level data structure that describes the kernel's virtual memory layout:memory::mmu::KernelVirtualLayout. - The
BSPpart:src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rscontains a static instance ofKernelVirtualLayoutand makes it accessible throug the functionbsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout(). - The
aarch64part:src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rscontains the actualMMUdriver. It picks up theBSP's high-levelKernelVirtualLayoutand maps it using a64 KiBgranule.
Generic Kernel code: memory/mmu.rs
The descriptor types provided in this file are building blocks which help to describe attributes of different memory regions. For example, R/W, no-execute, cached/uncached, and so on.
The descriptors are agnostic of the hardware MMU's actual descriptors. Different BSPs can use
these types to produce a high-level description of the kernel's virtual memory layout. The actual
MMU driver for the real HW will consume these types as an input.
This way, we achieve a clean abstraction between BSP and _arch code, which allows exchanging one
without needing to adapt the other.
BSP: bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
This file contains an instance of KernelVirtualLayout, which stores the descriptors mentioned
previously. The BSP is the correct place to do this, because it has knowledge of the target
board's memory map.
The policy is to only describe regions that are not ordinary, normal chacheable DRAM. However, nothing prevents you from defining those too if you wish to. Here is an example for the device MMIO region:
RangeDescriptor {
name: "Device MMIO",
virtual_range: || {
RangeInclusive::new(memory::map::mmio::BASE, memory::map::mmio::END_INCLUSIVE)
},
translation: Translation::Identity,
attribute_fields: AttributeFields {
mem_attributes: MemAttributes::Device,
acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
execute_never: true,
},
},
KernelVirtualLayout itself implements the following method:
pub fn virt_addr_properties(
&self,
virt_addr: usize,
) -> Result<(usize, AttributeFields), &'static str>
It will be used by the _arch/aarch64's MMU code to request attributes for a virtual address and
the translation of the address. The function scans for a descriptor that contains the queried
address, and returns the respective findings for the first entry that is a hit. If no entry is
found, it returns default attributes for normal chacheable DRAM and the input address, hence telling
the MMU code that the requested address should be identity mapped.
Due to this default return, it is technicall not needed to define normal cacheable DRAM regions.
AArch64: _arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
This file contains the AArch64 MMU driver. The granule is hardcoded here (64 KiB page
descriptors).
The actual translation tables are stored in a global instance of the TranslationTables struct:
/// A table descriptor for 64 KiB aperture.
///
/// The output points to the next table.
#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
#[repr(transparent)]
struct TableDescriptor(u64);
/// A page descriptor with 64 KiB aperture.
///
/// The output points to physical memory.
#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
#[repr(transparent)]
struct PageDescriptor(u64);
/// Big monolithic struct for storing the translation tables. Individual levels must be 64 KiB
/// aligned, hence the "reverse" order of appearance.
#[repr(C)]
#[repr(align(65536))]
struct TranslationTables<const N: usize> {
/// Page descriptors, covering 64 KiB windows per entry.
lvl3: [[PageDescriptor; 8192]; N],
/// Table descriptors, covering 512 MiB windows.
lvl2: [TableDescriptor; N],
}
/// Usually evaluates to 1 GiB for RPi3 and 4 GiB for RPi 4.
const ENTRIES_512_MIB: usize = bsp::memory::mmu::addr_space_size() >> FIVETWELVE_MIB_SHIFT;
/// The translation tables.
///
/// # Safety
///
/// - Supposed to land in `.bss`. Therefore, ensure that they boil down to all "0" entries.
static mut TABLES: TranslationTables<{ ENTRIES_512_MIB }> = TranslationTables {
lvl3: [[PageDescriptor(0); 8192]; ENTRIES_512_MIB],
lvl2: [TableDescriptor(0); ENTRIES_512_MIB],
};
They are populated using bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout().virt_addr_properties() and a bunch of
utility functions that convert our own descriptors to the actual 64 bit integer entries needed by
the MMU hardware for the translation table arrays.
Each page descriptor has an entry (AttrIndex) that indexes into the MAIR_EL1 register, which
holds information about the cacheability of the respective page. We currently define normal
cacheable memory and device memory (which is not cached).
/// Setup function for the MAIR_EL1 register.
fn set_up_mair() {
// Define the memory types being mapped.
MAIR_EL1.write(
// Attribute 1 - Cacheable normal DRAM.
MAIR_EL1::Attr1_Normal_Outer::WriteBack_NonTransient_ReadWriteAlloc +
MAIR_EL1::Attr1_Normal_Inner::WriteBack_NonTransient_ReadWriteAlloc +
// Attribute 0 - Device.
MAIR_EL1::Attr0_Device::nonGathering_nonReordering_EarlyWriteAck,
);
}
Afterwards, the Translation Table Base Register 0 - EL1 is set up with the base address of the
lvl2 tables and the Translation Control Register - EL1 is configured.
Finally, the MMU is turned on through the System Control Register - EL1. The last step also
enables caching for data and instructions.
link.ld
We need to align the ro section to 64 KiB so that it doesn't overlap with the next section that
needs read/write attributes. This blows up the binary in size, but is a small price to pay
considering that it reduces the amount of static paging entries significantly, when compared to the
classical 4 KiB granule.
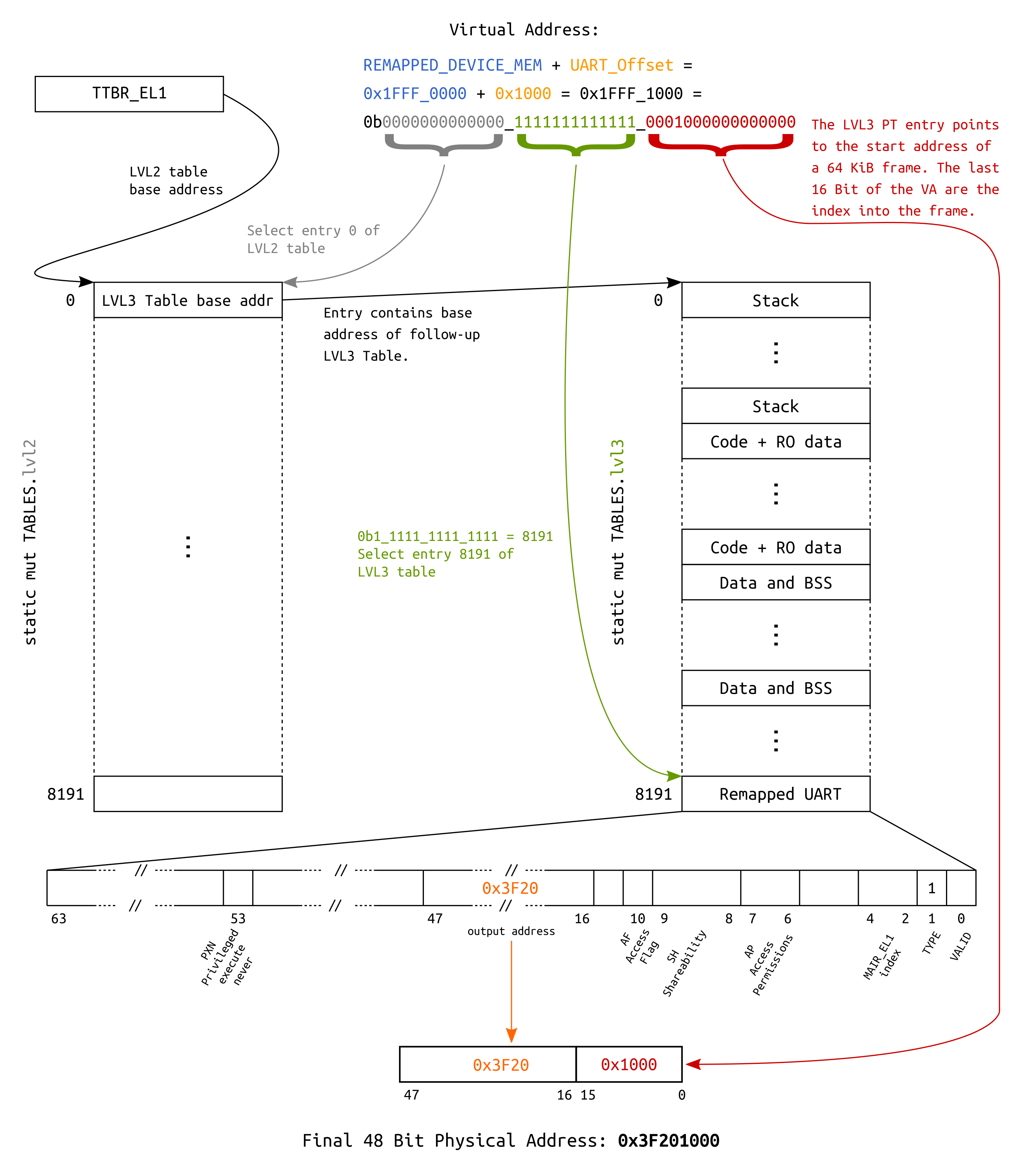
Address translation examples
For educational purposes, a layout is defined which allows to access the UART via two different
virtual addresses:
- Since we identity map the whole
Device MMIOregion, it is accessible by asserting its physical base address (0x3F20_1000or0xFA20_1000depending on which RPi you use) after theMMUis turned on. - Additionally, it is also mapped into the last
64 KiBentry of thelvl3table, making it accessible through base address0x1FFF_1000.
The following block diagram visualizes the underlying translation for the second mapping.
Address translation using a 64 KiB page descriptor
Zero-cost abstraction
The MMU init code is again a good example to see the great potential of Rust's zero-cost abstractions[1][2] for embedded programming.
Let's take a look again at the piece of code for setting up the MAIR_EL1 register using the
cortex-a crate:
/// Setup function for the MAIR_EL1 register.
fn set_up_mair() {
// Define the memory types being mapped.
MAIR_EL1.write(
// Attribute 1 - Cacheable normal DRAM.
MAIR_EL1::Attr1_Normal_Outer::WriteBack_NonTransient_ReadWriteAlloc +
MAIR_EL1::Attr1_Normal_Inner::WriteBack_NonTransient_ReadWriteAlloc +
// Attribute 0 - Device.
MAIR_EL1::Attr0_Device::nonGathering_nonReordering_EarlyWriteAck,
);
}
This piece of code is super expressive, and it makes use of traits, different types and
constants to provide type-safe register manipulation.
In the end, this code sets the first four bytes of the register to certain values according to the data sheet. Looking at the generated code, we can see that despite all the type-safety and abstractions, it boils down to two assembly instructions:
00000000000815e0 <kernel::memory::mmu::arch_mmu::MemoryManagementUnit as kernel::memory::mmu::interface::MMU>::init::hed32b31a58c93b32:
...
8161c: mov w8, #0xff04
...
81644: msr MAIR_EL1, x8
Test it
$ make chainboot
[...]
Minipush 1.0
[MP] ⏳ Waiting for /dev/ttyUSB0
[MP] ✅ Connected
__ __ _ _ _ _
| \/ (_)_ _ (_) | ___ __ _ __| |
| |\/| | | ' \| | |__/ _ \/ _` / _` |
|_| |_|_|_||_|_|____\___/\__,_\__,_|
Raspberry Pi 3
[ML] Requesting binary
[MP] ⏩ Pushing 64 KiB ========================================🦀 100% 32 KiB/s Time: 00:00:02
[ML] Loaded! Executing the payload now
[ 3.085343] Booting on: Raspberry Pi 3
[ 3.086427] MMU online. Special regions:
[ 3.088339] 0x00080000 - 0x0008ffff | 64 KiB | C RO PX | Kernel code and RO data
[ 3.092422] 0x1fff0000 - 0x1fffffff | 64 KiB | Dev RW PXN | Remapped Device MMIO
[ 3.096375] 0x3f000000 - 0x4000ffff | 16 MiB | Dev RW PXN | Device MMIO
[ 3.099937] Current privilege level: EL1
[ 3.101848] Exception handling state:
[ 3.103629] Debug: Masked
[ 3.105192] SError: Masked
[ 3.106756] IRQ: Masked
[ 3.108320] FIQ: Masked
[ 3.109884] Architectural timer resolution: 52 ns
[ 3.112186] Drivers loaded:
[ 3.113532] 1. BCM GPIO
[ 3.114966] 2. BCM PL011 UART
[ 3.116660] Timer test, spinning for 1 second
[ !!! ] Writing through the remapped UART at 0x1FFF_1000
[ 4.120828] Echoing input now
Diff to previous
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,319 @@
+// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
+//
+// Copyright (c) 2018-2020 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
+
+//! Memory Management Unit Driver.
+//!
+//! Static translation tables, compiled on boot; Everything 64 KiB granule.
+
+use super::{AccessPermissions, AttributeFields, MemAttributes};
+use crate::{bsp, memory};
+use core::convert;
+use cortex_a::{barrier, regs::*};
+use register::register_bitfields;
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Private Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+// A table descriptor, as per ARMv8-A Architecture Reference Manual Figure D5-15.
+register_bitfields! {u64,
+ STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR [
+ /// Physical address of the next descriptor.
+ NEXT_LEVEL_TABLE_ADDR_64KiB OFFSET(16) NUMBITS(32) [], // [47:16]
+
+ TYPE OFFSET(1) NUMBITS(1) [
+ Block = 0,
+ Table = 1
+ ],
+
+ VALID OFFSET(0) NUMBITS(1) [
+ False = 0,
+ True = 1
+ ]
+ ]
+}
+
+// A level 3 page descriptor, as per ARMv8-A Architecture Reference Manual Figure D5-17.
+register_bitfields! {u64,
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR [
+ /// Privileged execute-never.
+ PXN OFFSET(53) NUMBITS(1) [
+ False = 0,
+ True = 1
+ ],
+
+ /// Physical address of the next table descriptor (lvl2) or the page descriptor (lvl3).
+ OUTPUT_ADDR_64KiB OFFSET(16) NUMBITS(32) [], // [47:16]
+
+ /// Access flag.
+ AF OFFSET(10) NUMBITS(1) [
+ False = 0,
+ True = 1
+ ],
+
+ /// Shareability field.
+ SH OFFSET(8) NUMBITS(2) [
+ OuterShareable = 0b10,
+ InnerShareable = 0b11
+ ],
+
+ /// Access Permissions.
+ AP OFFSET(6) NUMBITS(2) [
+ RW_EL1 = 0b00,
+ RW_EL1_EL0 = 0b01,
+ RO_EL1 = 0b10,
+ RO_EL1_EL0 = 0b11
+ ],
+
+ /// Memory attributes index into the MAIR_EL1 register.
+ AttrIndx OFFSET(2) NUMBITS(3) [],
+
+ TYPE OFFSET(1) NUMBITS(1) [
+ Block = 0,
+ Table = 1
+ ],
+
+ VALID OFFSET(0) NUMBITS(1) [
+ False = 0,
+ True = 1
+ ]
+ ]
+}
+
+const SIXTYFOUR_KIB_SHIFT: usize = 16; // log2(64 * 1024)
+const FIVETWELVE_MIB_SHIFT: usize = 29; // log2(512 * 1024 * 1024)
+
+/// A table descriptor for 64 KiB aperture.
+///
+/// The output points to the next table.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+#[repr(transparent)]
+struct TableDescriptor(u64);
+
+/// A page descriptor with 64 KiB aperture.
+///
+/// The output points to physical memory.
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+#[repr(transparent)]
+struct PageDescriptor(u64);
+
+/// Big monolithic struct for storing the translation tables. Individual levels must be 64 KiB
+/// aligned, hence the "reverse" order of appearance.
+#[repr(C)]
+#[repr(align(65536))]
+struct TranslationTables<const N: usize> {
+ /// Page descriptors, covering 64 KiB windows per entry.
+ lvl3: [[PageDescriptor; 8192]; N],
+
+ /// Table descriptors, covering 512 MiB windows.
+ lvl2: [TableDescriptor; N],
+}
+
+/// Usually evaluates to 1 GiB for RPi3 and 4 GiB for RPi 4.
+const ENTRIES_512_MIB: usize = bsp::memory::mmu::addr_space_size() >> FIVETWELVE_MIB_SHIFT;
+
+/// The translation tables.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Supposed to land in `.bss`. Therefore, ensure that they boil down to all "0" entries.
+static mut TABLES: TranslationTables<{ ENTRIES_512_MIB }> = TranslationTables {
+ lvl3: [[PageDescriptor(0); 8192]; ENTRIES_512_MIB],
+ lvl2: [TableDescriptor(0); ENTRIES_512_MIB],
+};
+
+trait BaseAddr {
+ fn base_addr_u64(&self) -> u64;
+ fn base_addr_usize(&self) -> usize;
+}
+
+/// Constants for indexing the MAIR_EL1.
+#[allow(dead_code)]
+mod mair {
+ pub const DEVICE: u64 = 0;
+ pub const NORMAL: u64 = 1;
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Memory Management Unit type.
+pub struct MemoryManagementUnit;
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Global instances
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+static MMU: MemoryManagementUnit = MemoryManagementUnit;
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Private Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl<T, const N: usize> BaseAddr for [T; N] {
+ fn base_addr_u64(&self) -> u64 {
+ self as *const T as u64
+ }
+
+ fn base_addr_usize(&self) -> usize {
+ self as *const T as usize
+ }
+}
+
+impl convert::From<usize> for TableDescriptor {
+ fn from(next_lvl_table_addr: usize) -> Self {
+ let shifted = next_lvl_table_addr >> SIXTYFOUR_KIB_SHIFT;
+ let val = (STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR::VALID::True
+ + STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR::TYPE::Table
+ + STAGE1_TABLE_DESCRIPTOR::NEXT_LEVEL_TABLE_ADDR_64KiB.val(shifted as u64))
+ .value;
+
+ TableDescriptor(val)
+ }
+}
+
+/// Convert the kernel's generic memory range attributes to HW-specific attributes of the MMU.
+impl convert::From<AttributeFields>
+ for register::FieldValue<u64, STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::Register>
+{
+ fn from(attribute_fields: AttributeFields) -> Self {
+ // Memory attributes.
+ let mut desc = match attribute_fields.mem_attributes {
+ MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM => {
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::SH::InnerShareable
+ + STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::AttrIndx.val(mair::NORMAL)
+ }
+ MemAttributes::Device => {
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::SH::OuterShareable
+ + STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::AttrIndx.val(mair::DEVICE)
+ }
+ };
+
+ // Access Permissions.
+ desc += match attribute_fields.acc_perms {
+ AccessPermissions::ReadOnly => STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::AP::RO_EL1,
+ AccessPermissions::ReadWrite => STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::AP::RW_EL1,
+ };
+
+ // Execute Never.
+ desc += if attribute_fields.execute_never {
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::PXN::True
+ } else {
+ STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::PXN::False
+ };
+
+ desc
+ }
+}
+
+impl PageDescriptor {
+ fn new(output_addr: usize, attribute_fields: AttributeFields) -> Self {
+ let shifted = output_addr >> SIXTYFOUR_KIB_SHIFT;
+ let val = (STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::VALID::True
+ + STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::AF::True
+ + attribute_fields.into()
+ + STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::TYPE::Table
+ + STAGE1_PAGE_DESCRIPTOR::OUTPUT_ADDR_64KiB.val(shifted as u64))
+ .value;
+
+ Self(val)
+ }
+}
+
+/// Setup function for the MAIR_EL1 register.
+fn set_up_mair() {
+ // Define the memory types being mapped.
+ MAIR_EL1.write(
+ // Attribute 1 - Cacheable normal DRAM.
+ MAIR_EL1::Attr1_Normal_Outer::WriteBack_NonTransient_ReadWriteAlloc +
+ MAIR_EL1::Attr1_Normal_Inner::WriteBack_NonTransient_ReadWriteAlloc +
+
+ // Attribute 0 - Device.
+ MAIR_EL1::Attr0_Device::nonGathering_nonReordering_EarlyWriteAck,
+ );
+}
+
+/// Iterates over all static translation table entries and fills them at once.
+///
+/// # Safety
+///
+/// - Modifies a `static mut`. Ensure it only happens from here.
+unsafe fn populate_tt_entries() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ for (l2_nr, l2_entry) in TABLES.lvl2.iter_mut().enumerate() {
+ *l2_entry = TABLES.lvl3[l2_nr].base_addr_usize().into();
+
+ for (l3_nr, l3_entry) in TABLES.lvl3[l2_nr].iter_mut().enumerate() {
+ let virt_addr = (l2_nr << FIVETWELVE_MIB_SHIFT) + (l3_nr << SIXTYFOUR_KIB_SHIFT);
+
+ let (output_addr, attribute_fields) =
+ bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout().virt_addr_properties(virt_addr)?;
+
+ *l3_entry = PageDescriptor::new(output_addr, attribute_fields);
+ }
+ }
+
+ Ok(())
+}
+
+/// Configure various settings of stage 1 of the EL1 translation regime.
+fn configure_translation_control() {
+ let ips = ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1.read(ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1::PARange);
+ TCR_EL1.write(
+ TCR_EL1::TBI0::Ignored
+ + TCR_EL1::IPS.val(ips)
+ + TCR_EL1::TG0::KiB_64
+ + TCR_EL1::SH0::Inner
+ + TCR_EL1::ORGN0::WriteBack_ReadAlloc_WriteAlloc_Cacheable
+ + TCR_EL1::IRGN0::WriteBack_ReadAlloc_WriteAlloc_Cacheable
+ + TCR_EL1::EPD0::EnableTTBR0Walks
+ + TCR_EL1::T0SZ.val(32), // TTBR0 spans 4 GiB total.
+ );
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Return a reference to the MMU.
+pub fn mmu() -> &'static impl memory::mmu::interface::MMU {
+ &MMU
+}
+
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// OS Interface Code
+//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl memory::mmu::interface::MMU for MemoryManagementUnit {
+ unsafe fn init(&self) -> Result<(), &'static str> {
+ // Fail early if translation granule is not supported. Both RPis support it, though.
+ if !ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1.matches_all(ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1::TGran64::Supported) {
+ return Err("64 KiB translation granule not supported");
+ }
+
+ // Prepare the memory attribute indirection register.
+ set_up_mair();
+
+ // Populate translation tables.
+ populate_tt_entries()?;
+
+ // Set the "Translation Table Base Register".
+ TTBR0_EL1.set_baddr(TABLES.lvl2.base_addr_u64());
+
+ configure_translation_control();
+
+ // Switch the MMU on.
+ //
+ // First, force all previous changes to be seen before the MMU is enabled.
+ barrier::isb(barrier::SY);
+
+ // Enable the MMU and turn on data and instruction caching.
+ SCTLR_EL1.modify(SCTLR_EL1::M::Enable + SCTLR_EL1::C::Cacheable + SCTLR_EL1::I::Cacheable);
+
+ // Force MMU init to complete before next instruction.
+ barrier::isb(barrier::SY);
+
+ Ok(())
+ }
+}
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/bsp/raspberrypi/link.ld 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp/raspberrypi/link.ld
--- 10_privilege_level/src/bsp/raspberrypi/link.ld
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp/raspberrypi/link.ld
@@ -8,6 +8,7 @@
/* Set current address to the value from which the RPi starts execution */
. = 0x80000;
+ __ro_start = .;
.text :
{
*(.text._start) *(.text*)
@@ -17,6 +18,8 @@
{
*(.rodata*)
}
+ . = ALIGN(65536); /* Fill up to 64 KiB */
+ __ro_end = .;
.data :
{
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory/mmu.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
+//
+// Copyright (c) 2018-2020 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
+
+//! BSP Memory Management Unit.
+
+use super::map as memory_map;
+use crate::memory::mmu::*;
+use core::ops::RangeInclusive;
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+const NUM_MEM_RANGES: usize = 3;
+
+/// The virtual memory layout.
+///
+/// The layout must contain only special ranges, aka anything that is _not_ normal cacheable DRAM.
+/// It is agnostic of the paging granularity that the architecture's MMU will use.
+pub static LAYOUT: KernelVirtualLayout<{ NUM_MEM_RANGES }> = KernelVirtualLayout::new(
+ memory_map::END_INCLUSIVE,
+ [
+ RangeDescriptor {
+ name: "Kernel code and RO data",
+ virtual_range: || {
+ // Using the linker script, we ensure that the RO area is consecutive and 64 KiB
+ // aligned, and we export the boundaries via symbols:
+ //
+ // [__ro_start, __ro_end)
+ extern "C" {
+ // The inclusive start of the read-only area, aka the address of the first
+ // byte of the area.
+ static __ro_start: usize;
+
+ // The exclusive end of the read-only area, aka the address of the first
+ // byte _after_ the RO area.
+ static __ro_end: usize;
+ }
+
+ unsafe {
+ // Notice the subtraction to turn the exclusive end into an inclusive end.
+ #[allow(clippy::range_minus_one)]
+ RangeInclusive::new(
+ &__ro_start as *const _ as usize,
+ &__ro_end as *const _ as usize - 1,
+ )
+ }
+ },
+ translation: Translation::Identity,
+ attribute_fields: AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadOnly,
+ execute_never: false,
+ },
+ },
+ RangeDescriptor {
+ name: "Remapped Device MMIO",
+ virtual_range: || {
+ // The last 64 KiB slot in the first 512 MiB
+ RangeInclusive::new(0x1FFF_0000, 0x1FFF_FFFF)
+ },
+ translation: Translation::Offset(memory_map::mmio::BASE + 0x20_0000),
+ attribute_fields: AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::Device,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ },
+ },
+ RangeDescriptor {
+ name: "Device MMIO",
+ virtual_range: || {
+ RangeInclusive::new(memory_map::mmio::BASE, memory_map::mmio::END_INCLUSIVE)
+ },
+ translation: Translation::Identity,
+ attribute_fields: AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::Device,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ },
+ },
+ ],
+);
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Return the address space size in bytes.
+pub const fn addr_space_size() -> usize {
+ memory_map::END_INCLUSIVE + 1
+}
+
+/// Return a reference to the virtual memory layout.
+pub fn virt_mem_layout() -> &'static KernelVirtualLayout<{ NUM_MEM_RANGES }> {
+ &LAYOUT
+}
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp/raspberrypi/memory.rs
@@ -4,6 +4,8 @@
//! BSP Memory Management.
+pub mod mmu;
+
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Public Definitions
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -14,6 +16,8 @@
/// The board's memory map.
#[rustfmt::skip]
pub(super) mod map {
+ pub const END_INCLUSIVE: usize = 0xFFFF_FFFF;
+
pub const GPIO_OFFSET: usize = 0x0020_0000;
pub const UART_OFFSET: usize = 0x0020_1000;
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@
pub const BASE: usize = 0x3F00_0000;
pub const GPIO_BASE: usize = BASE + GPIO_OFFSET;
pub const PL011_UART_BASE: usize = BASE + UART_OFFSET;
+ pub const END_INCLUSIVE: usize = 0x4000_FFFF;
}
/// Physical devices.
@@ -35,5 +40,6 @@
pub const BASE: usize = 0xFE00_0000;
pub const GPIO_BASE: usize = BASE + GPIO_OFFSET;
pub const PL011_UART_BASE: usize = BASE + UART_OFFSET;
+ pub const END_INCLUSIVE: usize = 0xFF84_FFFF;
}
}
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/bsp.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/bsp.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/bsp.rs
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
//! Conditional re-exporting of Board Support Packages.
-mod device_driver;
+pub mod device_driver;
#[cfg(any(feature = "bsp_rpi3", feature = "bsp_rpi4"))]
mod raspberrypi;
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/main.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/main.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/main.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/main.rs
@@ -11,10 +11,12 @@
//!
//! - [`bsp::console::console()`] - Returns a reference to the kernel's [console interface].
//! - [`bsp::driver::driver_manager()`] - Returns a reference to the kernel's [driver interface].
+//! - [`memory::mmu::mmu()`] - Returns a reference to the kernel's [MMU interface].
//! - [`time::time_manager()`] - Returns a reference to the kernel's [timer interface].
//!
//! [console interface]: ../libkernel/console/interface/index.html
//! [driver interface]: ../libkernel/driver/interface/trait.DriverManager.html
+//! [MMU interface]: ../libkernel/memory/mmu/interface/trait.MMU.html
//! [timer interface]: ../libkernel/time/interface/trait.TimeManager.html
//!
//! # Code organization and architecture
@@ -102,6 +104,8 @@
//! - `crate::memory::*`
//! - `crate::bsp::memory::*`
+#![allow(incomplete_features)]
+#![feature(const_generics)]
#![feature(format_args_nl)]
#![feature(naked_functions)]
#![feature(panic_info_message)]
@@ -129,9 +133,18 @@
/// # Safety
///
/// - Only a single core must be active and running this function.
-/// - The init calls in this function must appear in the correct order.
+/// - The init calls in this function must appear in the correct order:
+/// - Virtual memory must be activated before the device drivers.
+/// - Without it, any atomic operations, e.g. the yet-to-be-introduced spinlocks in the device
+/// drivers (which currently employ NullLocks instead of spinlocks), will fail to work on
+/// the RPi SoCs.
unsafe fn kernel_init() -> ! {
use driver::interface::DriverManager;
+ use memory::mmu::interface::MMU;
+
+ if let Err(string) = memory::mmu::mmu().init() {
+ panic!("MMU: {}", string);
+ }
for i in bsp::driver::driver_manager().all_device_drivers().iter() {
if i.init().is_err() {
@@ -154,6 +167,9 @@
info!("Booting on: {}", bsp::board_name());
+ info!("MMU online. Special regions:");
+ bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout().print_layout();
+
let (_, privilege_level) = exception::current_privilege_level();
info!("Current privilege level: {}", privilege_level);
@@ -177,6 +193,13 @@
info!("Timer test, spinning for 1 second");
time::time_manager().spin_for(Duration::from_secs(1));
+ let remapped_uart = unsafe { bsp::device_driver::PL011Uart::new(0x1FFF_1000) };
+ writeln!(
+ remapped_uart,
+ "[ !!! ] Writing through the remapped UART at 0x1FFF_1000"
+ )
+ .unwrap();
+
info!("Echoing input now");
loop {
let c = bsp::console::console().read_char();
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/memory/mmu.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/memory/mmu.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/memory/mmu.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/memory/mmu.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,198 @@
+// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT OR Apache-2.0
+//
+// Copyright (c) 2020 Andre Richter <andre.o.richter@gmail.com>
+
+//! Memory Management Unit.
+//!
+//! In order to decouple `BSP` and `arch` parts of the MMU code (to keep them pluggable), this file
+//! provides types for composing an architecture-agnostic description of the kernel 's virtual
+//! memory layout.
+//!
+//! The `BSP` provides such a description through the `bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout()`
+//! function.
+//!
+//! The `MMU` driver of the `arch` code uses `bsp::memory::mmu::virt_mem_layout()` to compile and
+//! install respective translation tables.
+
+#[cfg(target_arch = "aarch64")]
+#[path = "../_arch/aarch64/memory/mmu.rs"]
+mod arch_mmu;
+pub use arch_mmu::*;
+
+use core::{fmt, ops::RangeInclusive};
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Definitions
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+/// Memory Management interfaces.
+pub mod interface {
+
+ /// MMU functions.
+ pub trait MMU {
+ /// Called by the kernel during early init. Supposed to take the translation tables from the
+ /// `BSP`-supplied `virt_mem_layout()` and install/activate them for the respective MMU.
+ ///
+ /// # Safety
+ ///
+ /// - Changes the HW's global state.
+ unsafe fn init(&self) -> Result<(), &'static str>;
+ }
+}
+
+/// Architecture agnostic translation types.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+pub enum Translation {
+ Identity,
+ Offset(usize),
+}
+
+/// Architecture agnostic memory attributes.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+pub enum MemAttributes {
+ CacheableDRAM,
+ Device,
+}
+
+/// Architecture agnostic access permissions.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+pub enum AccessPermissions {
+ ReadOnly,
+ ReadWrite,
+}
+
+/// Collection of memory attributes.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
+pub struct AttributeFields {
+ pub mem_attributes: MemAttributes,
+ pub acc_perms: AccessPermissions,
+ pub execute_never: bool,
+}
+
+/// Architecture agnostic descriptor for a memory range.
+#[allow(missing_docs)]
+pub struct RangeDescriptor {
+ pub name: &'static str,
+ pub virtual_range: fn() -> RangeInclusive<usize>,
+ pub translation: Translation,
+ pub attribute_fields: AttributeFields,
+}
+
+/// Type for expressing the kernel's virtual memory layout.
+pub struct KernelVirtualLayout<const NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES: usize> {
+ /// The last (inclusive) address of the address space.
+ max_virt_addr_inclusive: usize,
+
+ /// Array of descriptors for non-standard (normal cacheable DRAM) memory regions.
+ inner: [RangeDescriptor; NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES],
+}
+
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+// Public Code
+//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+impl Default for AttributeFields {
+ fn default() -> AttributeFields {
+ AttributeFields {
+ mem_attributes: MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM,
+ acc_perms: AccessPermissions::ReadWrite,
+ execute_never: true,
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+/// Human-readable output of a RangeDescriptor.
+impl fmt::Display for RangeDescriptor {
+ fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
+ // Call the function to which self.range points, and dereference the result, which causes
+ // Rust to copy the value.
+ let start = *(self.virtual_range)().start();
+ let end = *(self.virtual_range)().end();
+ let size = end - start + 1;
+
+ // log2(1024).
+ const KIB_RSHIFT: u32 = 10;
+
+ // log2(1024 * 1024).
+ const MIB_RSHIFT: u32 = 20;
+
+ let (size, unit) = if (size >> MIB_RSHIFT) > 0 {
+ (size >> MIB_RSHIFT, "MiB")
+ } else if (size >> KIB_RSHIFT) > 0 {
+ (size >> KIB_RSHIFT, "KiB")
+ } else {
+ (size, "Byte")
+ };
+
+ let attr = match self.attribute_fields.mem_attributes {
+ MemAttributes::CacheableDRAM => "C",
+ MemAttributes::Device => "Dev",
+ };
+
+ let acc_p = match self.attribute_fields.acc_perms {
+ AccessPermissions::ReadOnly => "RO",
+ AccessPermissions::ReadWrite => "RW",
+ };
+
+ let xn = if self.attribute_fields.execute_never {
+ "PXN"
+ } else {
+ "PX"
+ };
+
+ write!(
+ f,
+ " {:#010x} - {:#010x} | {: >3} {} | {: <3} {} {: <3} | {}",
+ start, end, size, unit, attr, acc_p, xn, self.name
+ )
+ }
+}
+
+impl<const NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES: usize> KernelVirtualLayout<{ NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES }> {
+ /// Create a new instance.
+ pub const fn new(max: usize, layout: [RangeDescriptor; NUM_SPECIAL_RANGES]) -> Self {
+ Self {
+ max_virt_addr_inclusive: max,
+ inner: layout,
+ }
+ }
+
+ /// For a virtual address, find and return the output address and corresponding attributes.
+ ///
+ /// If the address is not found in `inner`, return an identity mapped default with normal
+ /// cacheable DRAM attributes.
+ pub fn virt_addr_properties(
+ &self,
+ virt_addr: usize,
+ ) -> Result<(usize, AttributeFields), &'static str> {
+ if virt_addr > self.max_virt_addr_inclusive {
+ return Err("Address out of range");
+ }
+
+ for i in self.inner.iter() {
+ if (i.virtual_range)().contains(&virt_addr) {
+ let output_addr = match i.translation {
+ Translation::Identity => virt_addr,
+ Translation::Offset(a) => a + (virt_addr - (i.virtual_range)().start()),
+ };
+
+ return Ok((output_addr, i.attribute_fields));
+ }
+ }
+
+ Ok((virt_addr, AttributeFields::default()))
+ }
+
+ /// Print the memory layout.
+ pub fn print_layout(&self) {
+ use crate::info;
+
+ for i in self.inner.iter() {
+ info!("{}", i);
+ }
+ }
+}
diff -uNr 10_privilege_level/src/memory.rs 11_virtual_memory/src/memory.rs
--- 10_privilege_level/src/memory.rs
+++ 11_virtual_memory/src/memory.rs
@@ -4,6 +4,8 @@
//! Memory Management.
+pub mod mmu;
+
use core::ops::Range;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------